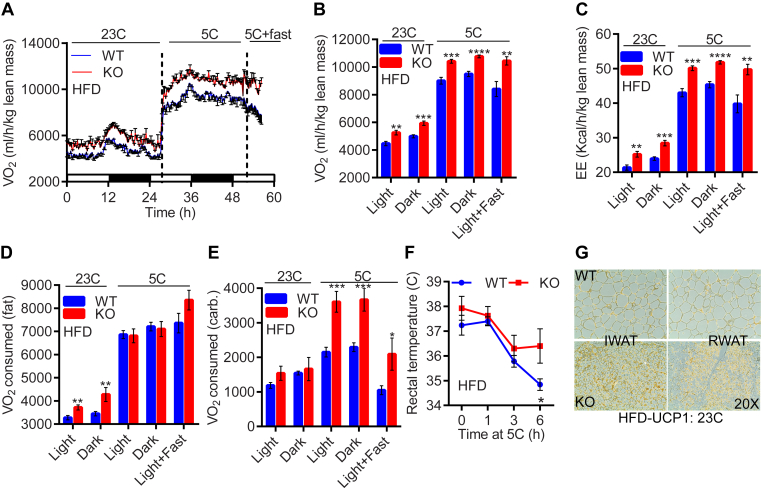
Figure 3.
HFD-fed IP6K1-KO mice exhibit higher fat oxidation at 23°C, albeit switch to carbohydrate oxidation at 5°C. A. HFD-KOs consume more oxygen than WT, both at 23 °C and 5 °C (n = 6–9 mice/group). B and C. Average VO2 and EE are enhanced in HFD-KOs under both temperature conditions (n = 6–9 mice/group; t-test). D and E. At 23 °C, HFD-KO mice oxidize more fat. However, cold exposed HFD-KOs switch to carbohydrate oxidation (n = 6–9 mice/group; t-test). F. Cold exposure decreases body temperature in HFD-WT whereas the knockouts are protected (n = 4–5 mice/group; two-way Anova). G. Immunohistochemistry reveals higher UCP1 protein levels in RWAT and IWAT of HFD-KOs. In all panels, data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.