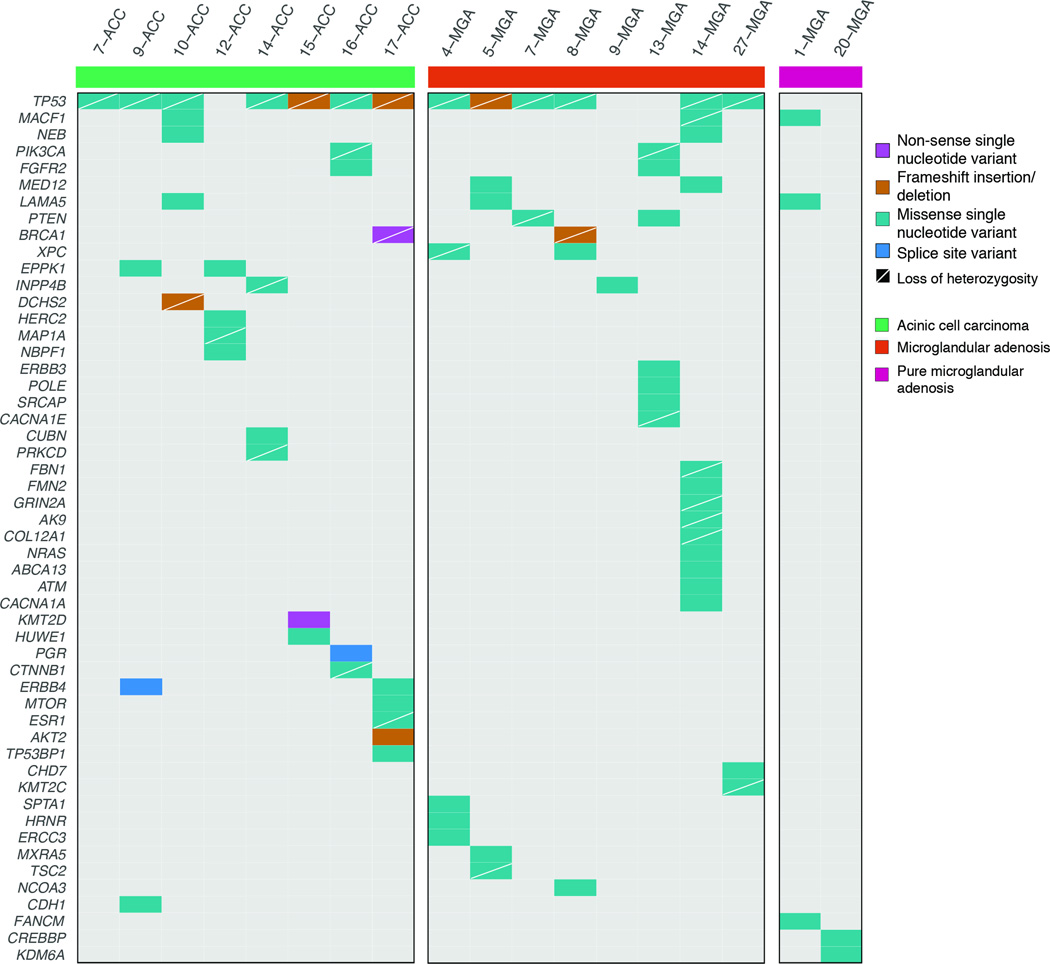
Figure 2. Non-synonymous somatic mutations detected by targeted capture massively parallel sequencing in microglandular adenoses and acinic cell carcinomas.
Heatmap indicating the non-synonymous somatic mutations identified in the pure microglandular adenoses (n=2), carcinoma-associated microglandular adenoses/atypical microglandular adenoses (n=8) and acinic cell carcinomas (n=8) analyzed. Each column represents one sample; mutated genes are reported in rows. Mutation types are color-coded according to the legend. The presence of loss of heterozygosity of the wild-type allele of a mutated gene is represented by a diagonal bar.