Figure 2.
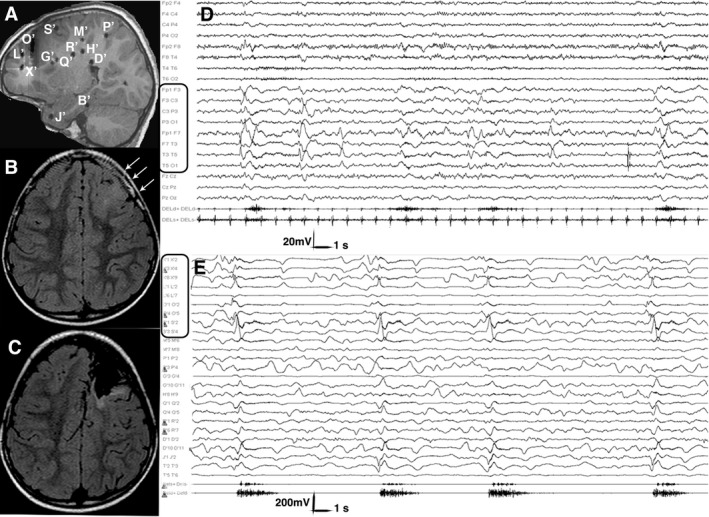
Postimplantation and Preoperative MRI, Scalp and Intracranial Ictal EEG. Patient 13, Table S1. (A) Post‐implantation sagittal T1‐weighted MRI showing the exact position of each electrode. Electrodes, labeled by uppercase letters, appear as either circles or lines, depending on the orthogonal or oblique trajectory. (B) Preoperative axial FLAIR MRI showing a left frontal area of cortical thickening, abnormal folding and increased signal intensity extending from the pole to the rolandic area, consistent with FCD (white arrows). (C) Postoperative axial FLAIR MRI showing the extent of resection. The primary motor area was spared, due to functional constraints. (D) Scalp ictal EEG during a cluster of asymmetric spasms. Ictal activity involves the left fronto‐temporal leads. Electromyogram shows a stronger contraction of the right deltoid during spasms. (E) Intracranial ictal EEG during a cluster of asymmetric spasms. Electrodes exploring the lesion (i.e. electrodes X’, L’, O’ and S’; black rectangles) are involved by initial ictal activity at spasm onset. Electromyogram shows again a stronger contraction of the right deltoid accompanying each spasm. Electrodes are labeled as in the postimplantation MRI. FCD, focal cortical dysplasia; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
