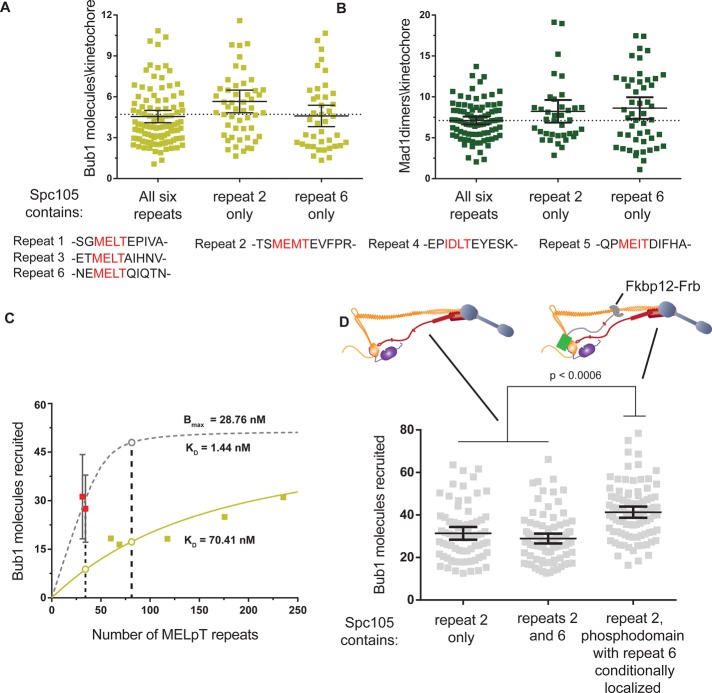
FIGURE 4:
Binding of more than one Bub3-Bub1 molecule to an Spc105 phosphodomain is strongly disfavored. (A) Comparison of the number of Bub1-GFP molecules recruited per kinetochore in nocodazole-treated cells expressing wild-type Spc105 with those expressing Spc105-5A(172T) or Spc105-5A(313T) (mean ± 95% confidence intervals). Differences in mean values are not statistically significant. The sequences of the MELT repeats are noted at the bottom for comparison. (B) Comparison of the recruitment of Mad1-GFP under the same conditions as in A. Differences in mean values are not statistically significant. (C) Binding curves for MELpT and Bub3-Bub1 suggested by wild-type Spc105 (pale green) and the Spc105-5A alleles (dashed gray). Data from Figure 2C were replotted by converting the total number of Spc105 molecules in the cluster of unattached kinetochores into the number of MELpT repeats. The dashed curve displays the binding of Bub1 predicted by the affinity of spc105-5A molecules and the Bmax from Figure 2C. The open circles highlight the expected recruitment of Bub3-Bub1 as a function of the number of MELT repeats predicted by the two models. (D) Top, the two experimental schemes used to double the total number of MELT repeats in the kinetochore. Left, each Spc105 molecule contains two phosphorylatable MELT repeats. Right, in a strain expressing Spc105-5A(172T), rapamycin-induced dimerization of GFP-Spc105120:329-5A(313T)-Frb with Ndc80-2xFkbp12 is used to create kinetochores that contain twice as many phosphodomains as a wild-type cell. Because each phosphodomain contains one MELT motif, the number of MELT motifs per kinetochore is also doubled. Bottom, comparison of Bub1 recruitment by the indicated Spc105 alleles (mean ± 95% confidence intervals).