FIGURE 2:
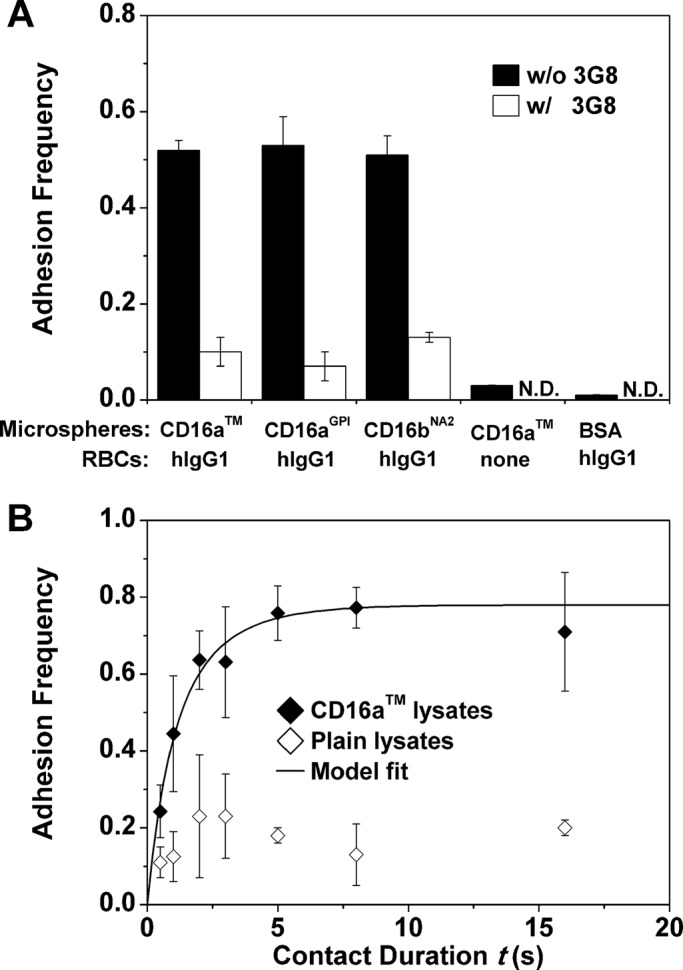
Microspheres bearing CD16 bound RBCs coated with hIgG1 specifically. (A) Adhesion frequency of CD16 lysate–coated microspheres to hIgG1-coated RBCs was substantially higher than the nonspecific adhesions, controlled using a blocking anti-CD16 (3G8) or microspheres incubated with BSA (instead of lysates of CD16 expressing CHO cells) or RBCs not coated with anything. N.D., not done. Adhesion frequencies were measured with a 2-s contact duration. (B) Adhesion frequency vs. contact duration (t) binding curves. The two sets of data (points) were obtained using RBCs coated with hIgG1 to contact 214.1-precoated microspheres incubated with lysates from CHO cells expressing CD16aTM (filled diamonds) or plain CHO cells (open diamonds). For the former, the specific adhesion frequency Pa after removing the nonspecific adhesion frequency (Eq. 1) is shown and fitted by Eq. 2 (curve). Data are mean ± SEM of five RBC-microsphere pairs with 100 contacts each per bar or point.
