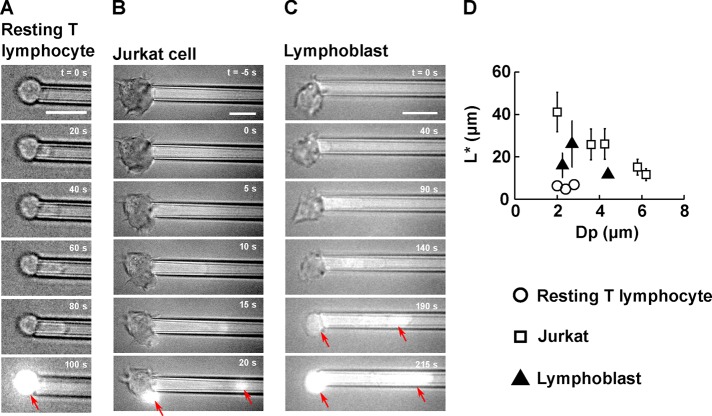
FIGURE 3:
T-lymphocyte membrane ruptures at a well-defined entry length L* during micropipette aspiration. (A–C) Example of membrane rupture triggered using micropipette aspiration for (A) a resting T-lymphocyte, (B) a Jurkat cell, and (C) a lymphoblast. Scale bar, 10 μm. The time is indicated in the top right-hand corner, with t = 0 s chosen as the time at which the aspiration pressure goes from −20 Pa to ΔP. A background of bright-field light is kept to visualize the cell throughout the experiment. On membrane rupture, propidium iodide enters the cell and binds to DNA, emitting a bright fluorescent signal (red arrows). (D) Plot of the entry length at rupture, L*, vs. micropipette diameter, Dp, for three cell types: resting T-lymphocytes (14 cells), Jurkat cells (27 cells), and lymphoblasts (14 cells). Bars represent SD.