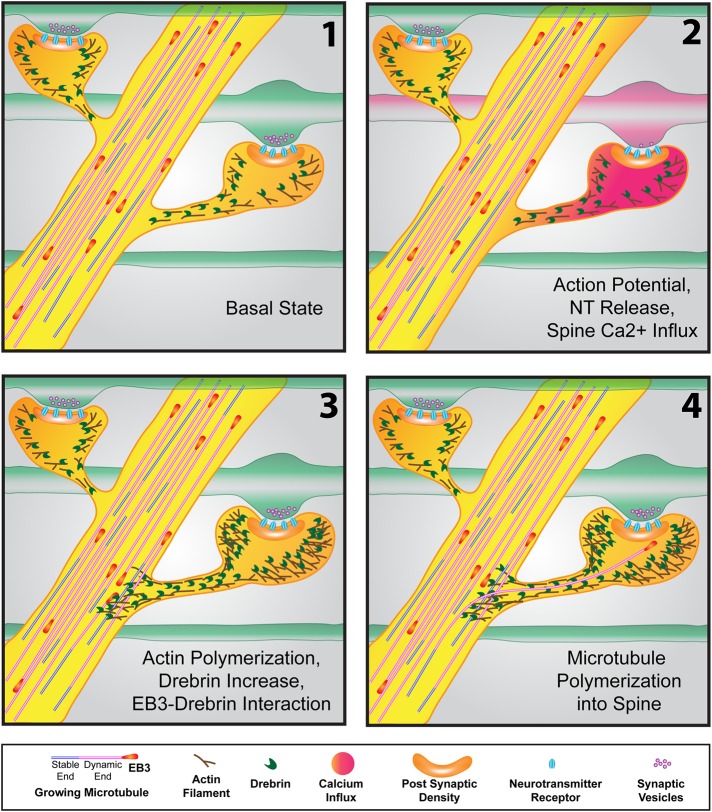
FIGURE 3:
Events resulting in microtubule polymerization into a dendritic spine. (1) In the basal state, microtubules, tipped by “comets” of +TIP proteins (EB3 shown here), actively polymerize throughout the dendrite (as well as the axon; not shown). Actin and the actin-binding protein drebrin are concentrated in spines. (2) As the action potential makes its way down an axon (red in second frame), resulting in neurotransmitter release at the synapse, calcium influx in the postsynaptic spine occurs. (3) Within seconds to minutes after calcium spikes in the spine, actin polymerization occurs in the spine head and neck and can extend into the dendritic shaft. The spine head increases in size due to the increased actin polymerization. Increased actin also concentrates drebrin, which interacts with EB3 protein at the tips of polymerizing microtubules in the vicinity of the spine. (4) This drebrin–EB3 interaction results in the increased probability that the polymerizing microtubule will enter the spine (on the right). The microtubule can extend well into the spine head, often to the postsynaptic density.