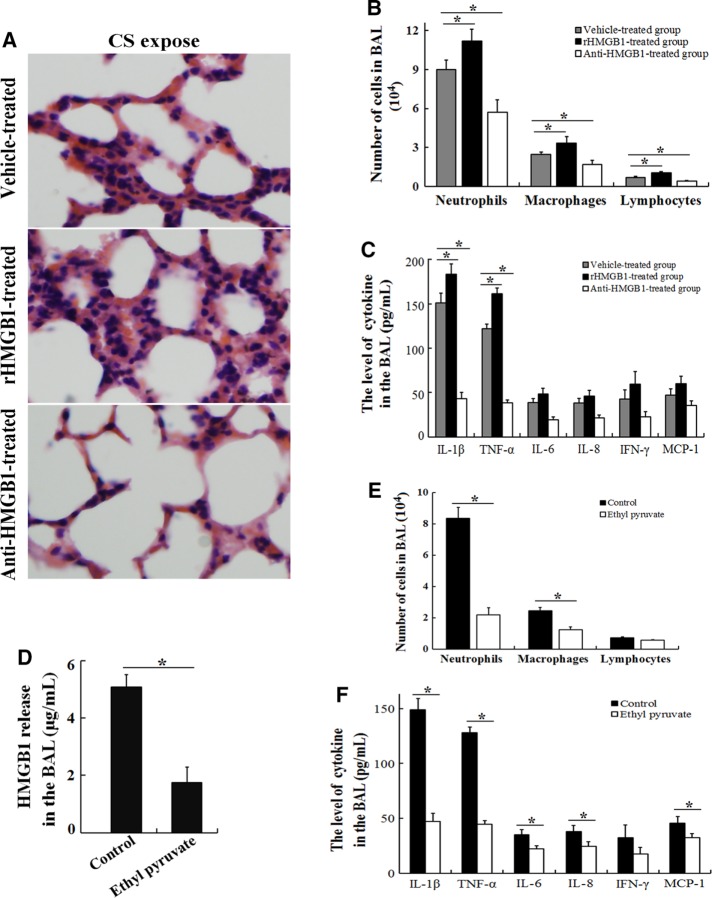
FIGURE 4:
HMGB1 controls the CS-induced inflammatory response in the lungs. C57BL/6 mice received an intravenous injection of 200 μg/kg rHMGB1, a neutralizing anti-HMGB1 antibody (10 mg/kg), or vehicle (PBS) via the tail vein each day (n = 6 for each group) during acute (3 d) exposure to CS. (A) The lungs were collected for hematoxylin and eosin staining, and the BAL fluid was obtained and used to measure (B) differential cell counts and (C) the differences in the proinflammatory cytokine concentrations. C57BL/6 mice were intravenously administered ethyl pyruvate (20 mg/kg; an inhibitor of HMGB1 release) or vehicle (PBS) during acute (3 d) exposure to CS (n = 5 for each group). Three days later, the BAL fluid was obtained and used to measure (D) HMGB1 release in the BAL, (E) differential cell counts, and (F) differences in the proinflammatory cytokine concentrations. The results are displayed as means ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05.