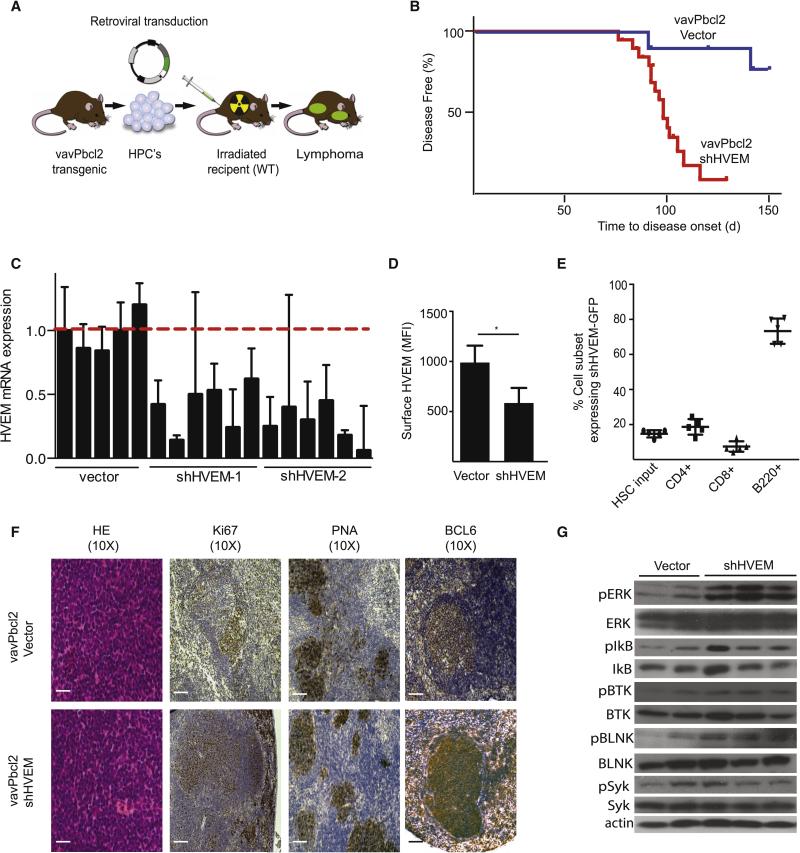
Figure 2. HVEM functions as a tumor suppressor in a mouse model of FL.
A, Schematic representation of vavPBcl2 mosaic mouse model; B, Kaplan-Meier analysis of disease free survival (blue: Vector, n=11; red: shRNA against HVEM, n=19); C, qRT-PCR analysis for relative HVEM expression on murine lymphomas; D, FACS quantification of HVEM surface expression in mouse tumors (n = 5, mean ± SD, *p < 0.01); E, Tracking expression of the shHVEM/GFP construct in indicated mouse cell populations, HSCs indicates initial infection efficiency before injection into mouse, (n=5); F, Representative pathology and immunohistochemistry for control (vavPBcl2/vector) and HVEM deficient (vavPBcl2/shHVEM) lymphomas, scale bars = 100 μm; G, Immunoblots for indicated signaling molecules on control (vector) and HVEM deficient (shHVEM) lymphomas. (See also Figure S2, and Table S6).