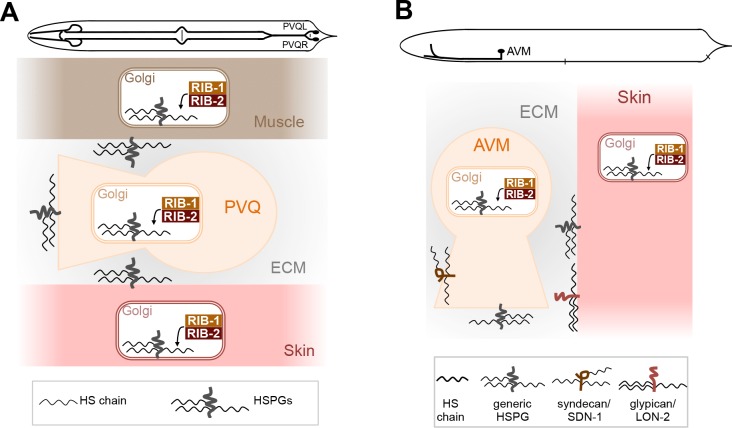
Fig 10. A model for the role of HSPGs in the guidance of PVQ and AVM axons.
A. The PVQ axons extend along the ventral nerve cord, following pioneer axons [96]. PVQ axons are in contact with the extracellular matrix and in close proximity to muscles and hypodermis (skin). For proper guidance of the PVQ axons, combined HS chain elongation from the muscles, skin, and neurons is required, suggesting that multiple HSPGs coordinate the guidance of the PVQ axon. B. The ventral axon guidance of AVM requires HS chain elongation from the migrating neuron itself, or from the skin, and HS chains are required for both unc-6/Netrin and slt-1/Slit guidance systems. Taken together with previous results, AVM is likely guided by HSPGs functioning from AVM (including sdn-1/Syndecan [8]), and HSPGs functioning from the skin, (including lon-2/Glypican [8]), as well as possibly other unidentified HSPGs.