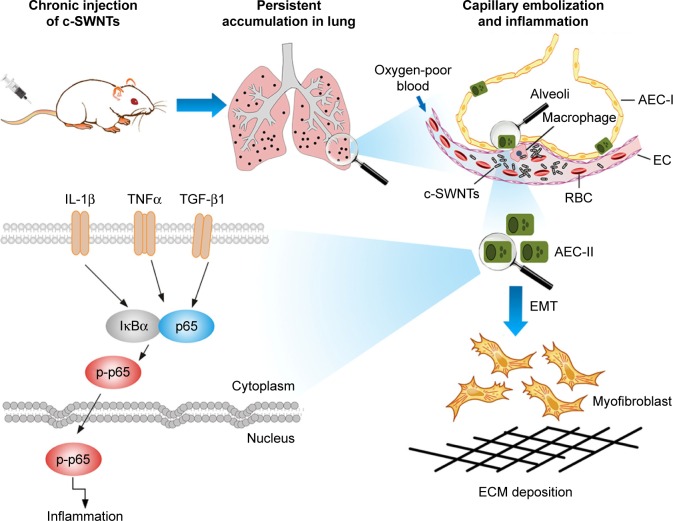
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis induced by long-term intravenous exposure to c-SWNTs.
Notes: Long-term intravenous injection induces persistent accumulation of c-SWNTs in rat lung, embolization in alveolar capillary, and inflammation regulated by NF-κB pathway, resulting in EMT of AECs-II and ECM deposition.
Abbreviations: c-SWNTs, carboxylated single-walled carbon nanotubes; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; AEC-II, alveolar epithelial cell type-II; ECM, extracellular matrix; AEC-I, alveolar epithelial cell type-I; RBC, red blood cell; EC, endothelial cell; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-beta 1; IκBα, inhibitor of kappa B alpha; p-p65, phosphorylated p65.