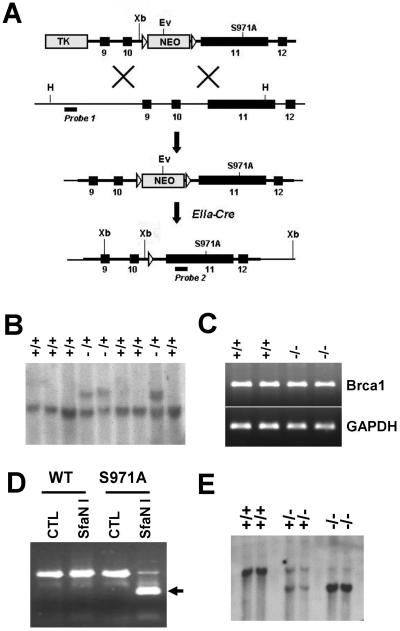
FIG. 1.
Introduction of the S971A mutation into mouse Brca1 locus. (A) Targeting vector and final structure of the mutant allele. The point mutation S971A in exon 11 was cotransferred with ploxPneo through homologous recombination in ES cells. Once germ line transmission was established, mice heterozygous for the mutation (+/S971A-neo) were crossed with EIIa-Cre transgenic mice to delete ploxPneo. H, HindIII; Ev, EcoRV; X, XhoI Xb, XbaI TK, thymidine kinase; open triangles, loxp sites. The positions of the probes used for Southern blot analyses and the sizes of the endogenous and targeted DNA fragments recognized by these probes are shown. (B) Southern analysis of ES cell DNA digested with HindIII to identify the targeting event that is characterized by a fragment shift from 10 to 12 kb due to the presence of neo. Same samples digested with HindIII and EcoRV were subjected to Southern analysis with an internal BamHI probe (data not shown). (C) Reverse transcription-PCR analysis to check the proper expression of Brca1 was performed in wild-type and Brca1S971A/S971A mutant MEFs by using primers against exon 11 of Brca1 with GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) control. (D) DNA fragments containing the S971A mutation were amplified by PCR, followed by digestion with SfaNI. The PCR product (500 bp) from S971A was cleaved by SfaNI (the cleaved fragment [250 bp] is indicated by an arrow). The presence of the mutation was also confirmed by sequencing of the PCR product (data not shown). WT, wild type. (E) Southern blot analysis of XbaI-digested tail DNA isolated from wild-type, heterozygous (+/S971A), and homozygous (S971A/S971A) mice after neo excision. The presence of a 7-kb fragment by Southern blotting represented the removal of neo.