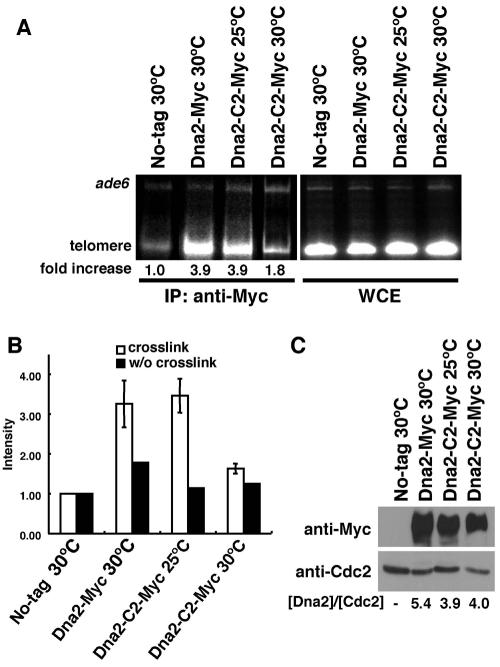
FIG. 4.
Binding of Dna2-C2 mutant protein to telomere DNA is severely impaired by a temperature shift to the semipermissive temperature. (A) ChIP assay of the Dna2 protein. Untagged wild-type control cells (JY741), dna2-myc (KTtnM) cells, and dna2-C2-myc (KTtnMM1) cells were cultured at the indicated temperatures. PCRs were performed on whole-cell extract (WCE; input) and on chromatin immunoprecipitates (IP: anti-Myc) with primers to amplify telomere DNA (telomere) and DNA from the ade6+ gene (ade6). The relative enrichment of precipitated telomere DNA is shown underneath each lane. Ratios of telomere signals to ade6 signals were used to calculate relative precipitation enrichment. (B) Relative precipitation enrichment determined in the ChIP assay shown in panel A. Error bars, standard deviations determined from four independent experiments. As a control, the ChIP assay was performed without (w/o) cross-linking. (C) Protein expression level is not affected in the dna2-C2 mutant at the permissive temperature versus the semipermissive temperature. The Dna2-Myc protein from dna2-myc cells (KTtnM) and the Dna2-C2-Myc protein from dna2-C2-myc cells (KTtnMM1) were detected by Western blotting with the anti-Myc 9B11 antibody (Cell Signaling). As a control, Cdc2 was also detected with an anti-Cdc2 antibody (PSTAIRE). The relative amounts of Dna2 or Dna2-C2 are shown underneath each lane. Ratios of Dna2 or Dna2-C2 signals to Cdc2 signals were calculated to express the relative amounts of Dna2 and Dna2-C2.