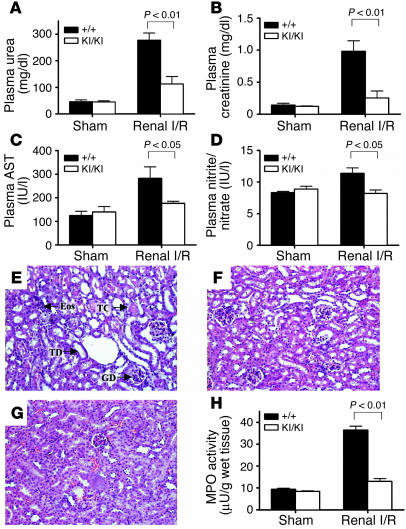
Figure 7.
PARP-1 KI/KI mice are protected from renal I/R. (A–D) Biochemical parameters of mice subjected to sham-operation or renal I/R. (A) Plasma urea and (B) creatinine levels were measured as markers of renal dysfunction. (C) Plasma AST levels were measured as a marker of reperfusion injury. (D) Plasma nitrite/nitrate levels were measured as a marker of nitric oxide synthesis. (E–G) Histological analysis (H&E) of renal sections of mice subjected to sham-operation or renal I/R. (E) A renal section of a wild-type mouse subjected to renal I/R showing glomerular degeneration (GD), tubular dilatation (TD), tubular congestion (TC), and the presence of eosinophilia (Eos). (F) A PARP-1KI/KI kidney after renal I/R displayed a reduction in renal injury. (G) A section from a sham-operated mouse. Original magnification, ×125. (H) Renal MPO activity was measured as a marker of neutrophil infiltration subsequent to sham operation or renal I/R. Wild-type sham: n = 6; PARP-1KI/KI sham: n = 4; wild-type renal I/R: n = 8; PARP-1KI/KI renal I/R: n = 8. Data in A–D and H represent the mean ± SEM for n observations.