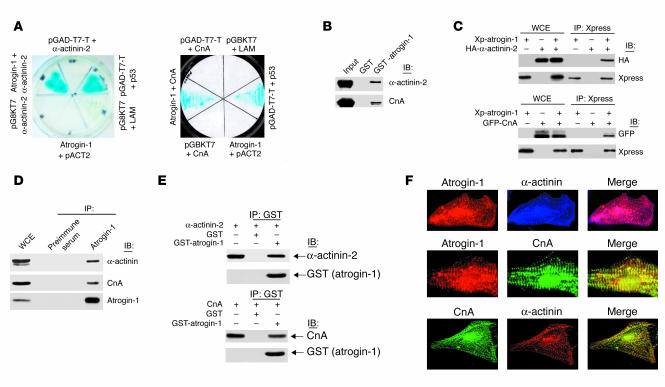
Figure 1.
Molecular interaction of atrogin-1 with α-actinin-2 and calcineurin A (CnA). (A) Yeast 2-hybrid analysis of atrogin-1 interaction with α-actinin-2 (left) and calcineurin A (right). pGBKT7 and pACT2 are empty plasmids. pGAD-T7 vector expresses a T antigen–GAL4 activation domain fusion that interacts with p53 (positive control reaction). (B) In vitro interactions of atrogin-1 with α-actinin-2 and calcineurin A in GST pull-down assays. The ability of α-actinin-2 (top) or calcineurin A (bottom) expressed in COS-7 cells to be retained by GST or a GST–atrogin-1 fusion protein was analyzed by immunoblotting after binding reactions. (C) COS-7 cells were transfected with Xpress-tagged (Xp) atrogin-1 and GFP-tagged calcineurin A or HA-tagged α-actinin-2 expression plasmids as indicated. Equal amounts of cell extract were immunoprecipitated with the Xpress antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies directed against Xpress (to detect atrogin-1) and HA (to detect α-actinin-2, top) or against GFP (to detect calcineurin A, bottom). WCE, whole cell extract. (D) Endogenous protein interactions were examined in cardiomyocyte cell lysates that were immunoprecipitated with preimmune serum or anti–atrogin-1 antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to detect α-actinin (top), calcineurin A (middle), and atrogin-1 (bottom). (E) Direct protein interactions were detected by incubation of GST–atrogin-1 or GST (1 μg) with 1 μg of recombinant calcineurin A or α-actinin-2 proteins. Mixtures were precipitated with anti-GST antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against α-actinin, calcineurin A, and GST. (F) Coimmunostaining analysis of endogenous atrogin-1, calcineurin A, and α-actinin-2 in neonatal cardiomyocytes. The overlay shows that atrogin-1 colocalizes with both α-actinin (top) and calcineurin A (middle).