Figure 4.
High-Resolution Structure of the Zn Finger Array of Cep104
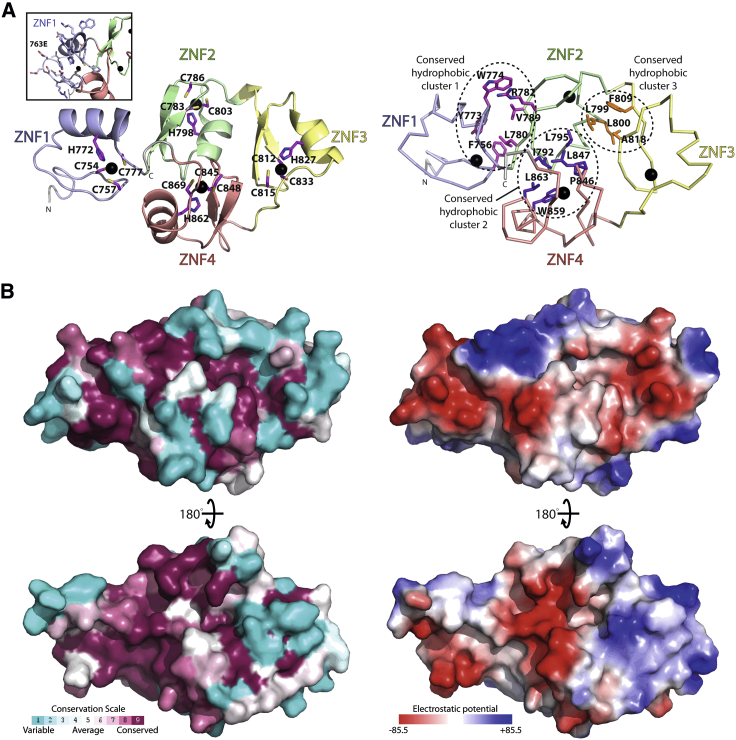
(A) The Cep104 ZNFs adopt an overall globular domain. Left: ribbon presentation of the human Cep104 ZNF array structure (Cep104746−875 S763E). The individual Zn fingers are colored distinctly. The Zn-coordinating side chains in the ZNFs are shown as sticks and labeled, the coordinated Zn ions are displayed as black spheres. Inset: close-up of ZNF1 with side chains displayed as sticks. Note that the S763E mutation that was used to improve solubility of the Cep104 ZNF domain is located in a loop and does not make contact with the rest of the domain. This residue is poorly conserved (Figure S6A). Right: similar view of the Cep104 ZNF domain. Labeled and shown as sticks are the side chains of the three conserved hydrophobic clusters in the interfaces between the individual ZNFs (Figure S6A). These clusters maintain the overall globular packing of the ZNF array.
(B) Top: similar view as in (A) but as a molecular surface colored according to CONSURF evolutionary conservation score (left) from unconserved (cyan) to highly conserved (burgundy), or colored according to in vacuo electrostatic potential (right) from positive (blue) to negative potential (red). Bottom: rotated 180° as indicated.
See also Figure S6.