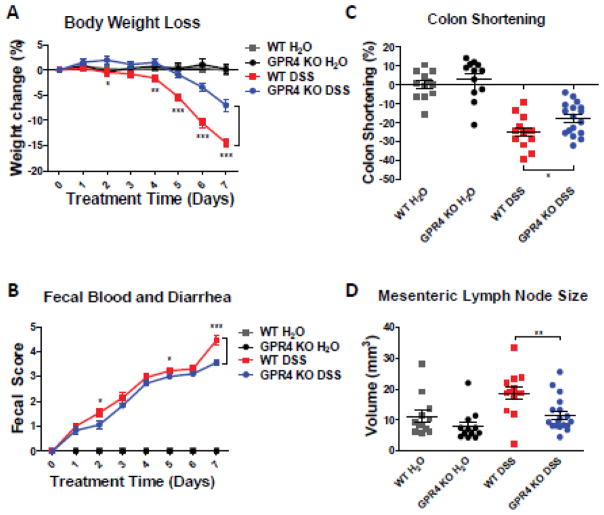
Fig. 1.
Clinical phenotypes and macroscopic indicators. To assess the extent of DSS-induced colitic inflammation in mice, we measured several parameters to gauge the disease severity in mice. We observed GPR4 KO-DSS mice had reduced disease severity when compared to WT-DSS mice. Clinical parameters of disease severity, including (A) body weight loss, (B) colon shortening, (C) fecal score and (D) mesenteric lymph node volume, were assessed in WT-control (n=12), WT-DSS (n=13), GPR4 KO-control (n=12), and GPR4 KO-DSS (n=18) mice. Each dot represents the data from an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and was analyzed for statistical significance using the unpaired t-test between WT-DSS mice and GPR4 KO-DSS mice or as indicated within graph. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *** P< 0.001).