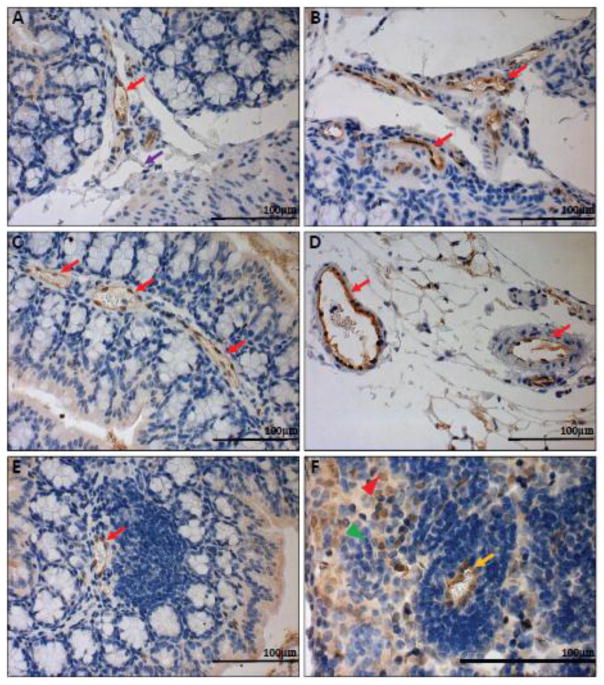
Fig. 6.
GFP knock-in as a surrogate marker for GPR4 expression in GPR4 KO control mouse colon and lymphoid tissues. To assess the localization of GPR4 in intestinal tissues, we performed IHC of GFP in intestinal and lymph tissues. GFP expression was visualized as brown signals in the intestinal microvascular endothelial cells, ex-mural blood vessels, and mesenteric lymph node high endothelial venules (HEVs). GFP expression was barely detectable in lymphatic ECs. (A–B) Colonic GPR4 KO-control mouse blood vessel, artery, and lymphatic vessel, (C) transverse fold microvessels, (D) ex-mural blood vessel and arteries, (E) microvessels adjacent to isolated lymphoid follicles, and (F) mesenteric lymph node HEVs and histiocytes. No GFP signal detected in WT untreated control tissues (Supplementary Fig. S7). (A–E) 40× and (F) 63× microscope objectives. Red arrow heads indicate histiocytes (macrophages) and green arrow heads indicates lymphocytes. Red arrows indicate blood vessels, yellow arrows indicate HEVs, and purple arrows indicate lymphatics.