Figure 4.
Lysosomal Ca2+ Signaling Drives Fusion of the Lysosomes with the Plasma Membrane
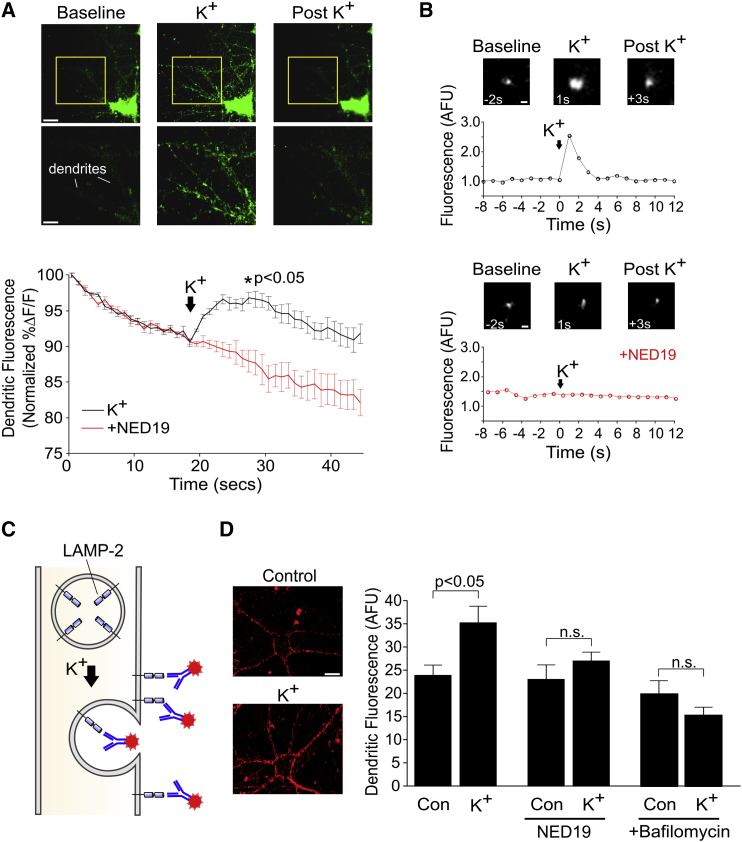
(A) Top: TIRFM images of a dissociated hippocampal neuron loaded with LysoTracker. K+ stimulation resulted in translocation of LysoTracker-stained puncta to the cell surface (scale bar, 10 μm). The imaged area in the yellow box is magnified below (scale bar, 5 μm). Bottom: average change in LysoTracker fluorescence across time (n = 5 cells/condition). K+-induced increases in fluorescence were abolished by NED-19. Time-dependent decreases in fluorescence reflected photobleaching. Significance was assessed with Mann-Whitney test at the peak of fluorescence.
(B) Sample TIRFM images of individual LysoTracker-stained puncta in (A) (scale bar, 2 μm). Graphs depict fluorescence intensity in AFU against time.
(C) Schematic of live-cell immunolabeling of LAMP-2. Fluorescently tagged antibodies targeting the lumenal domain of LAMP-2 were applied to neuronal cultures during K+ stimulation. Fluorescent labeling would require fusion of the lysosome with the plasma membrane.
(D) Left: sample images depicting surface LAMP-2 antibody labeling in dissociated hippocampal cultures (scale bar, 10 μm). Labeling in K+-treated cultures was greater than under control conditions. Right: the graph depicts group averages of LAMP-2 labeling (n = 10–23 cells/condition). NED-19 and bafilomycin prevented activity-dependent increases in LAMP-2 labeling.
Significance was assessed with Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Dunn’s tests. Error bars represent SEM. See also Figure S6 and Movie S1.