Figure 5.
Imaging Lysosomal Fusion with LAMP2-SEP
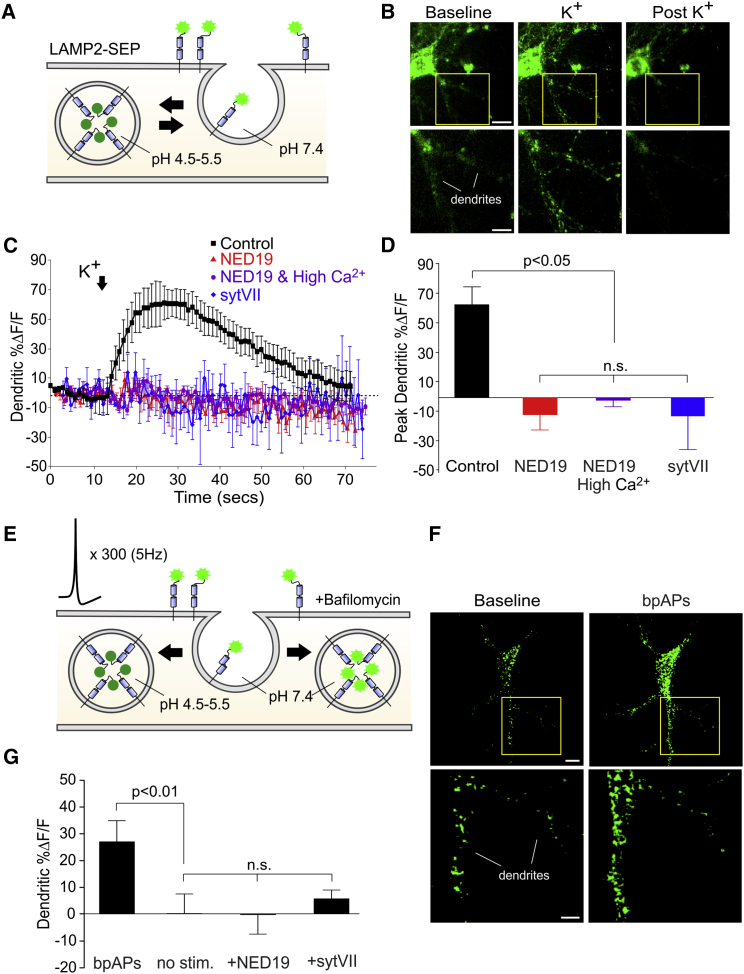
(A) Schematic of LAMP2-SEP. pH-dependent changes in fluorescence were used to monitor lysosomal fusion.
(B) TIRFM image of a dissociated hippocampal neuron transfected with LAMP2-SEP (scale bar, 10 μm). The imaged area in the yellow box is magnified below (scale bar, 5 μm).
(C and D) Average K+-evoked changes in LAMP2-SEP fluorescence in time (D, n = 5–7 cells/condition) with peak changes quantified in (D). Activity-dependent increases in fluorescence were abolished by NED-19 or intracellular loading of Syt7.
(E) Schematic of the experiment using the alkaline trap to examine lysosome fusion in response to bpAPs. Neurons were stimulated with 300 action potentials at 5 Hz in the presence of bafilomycin to prevent re-acidification of the lysosome upon internalization.
(F) Confocal image of a dissociated neuron transfected with LAMP2-SEP (scale bar, 10 μm). The imaged area in the yellow box is magnified below (scale bar, 5 μm). bpAPs triggered an increase in fluorescence.
(G) Average bpAP-evoked change in LAMP2-SEP fluorescence (n = 6–7 cells/condition). No activity-dependent increases in fluorescence occurred following extracellular application of NED-19 or intracellular loading of Syt7.
Significance was assessed with Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Dunn’s tests. Error bars represent SEM. See also Figure S7 and Movie S2.