Fig. 1.
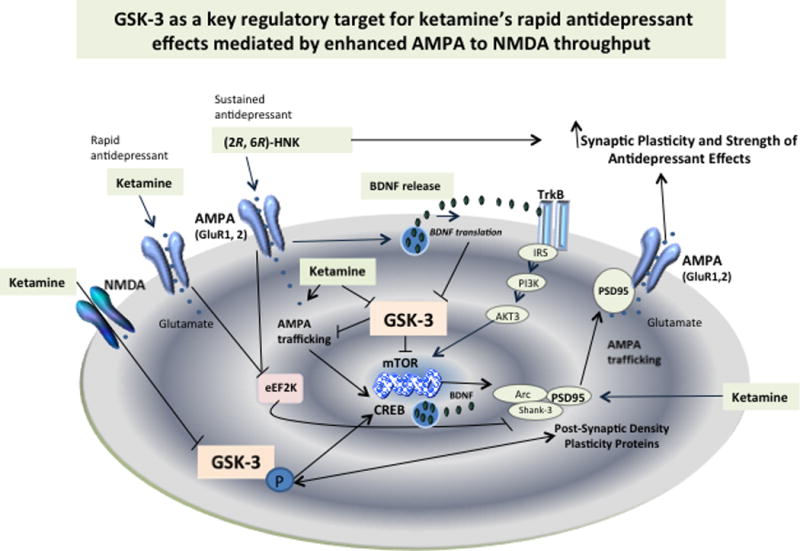
Enhanced AMPA to NMDA throughput is a key convergent model suggesting that augmentation of AMPA receptor signaling mediates the activation of synaptic plasticity and, consequently, the rapid antidepressant effects of the glutamatergic modulator ketamine. GSK-3 has been shown to critically regulate AMPA receptor activation and intracellular trafficking by limiting its activity and associated antidepressant efficacy. Increased GSK-3 phosphorylation by ketamine inactivates the protein and favors increases in mTOR, CREB, and PSD-95 expression. AMPA receptor trafficking is regulated by PSD-95, which also regulates GSK-3. Ketamine lowers phosphorylated PSD-95 on Thr-19, the GSK-3 target that promotes AMPA receptor internalization. Similar activation of synaptic strength and plasticity involving direct regulation at GSK-3 are expected to take place with the ketamine metabolite (2R, 6R)-HNK based on its direct ability to activate AMPA receptors and synaptogenesis in preclinical models.
