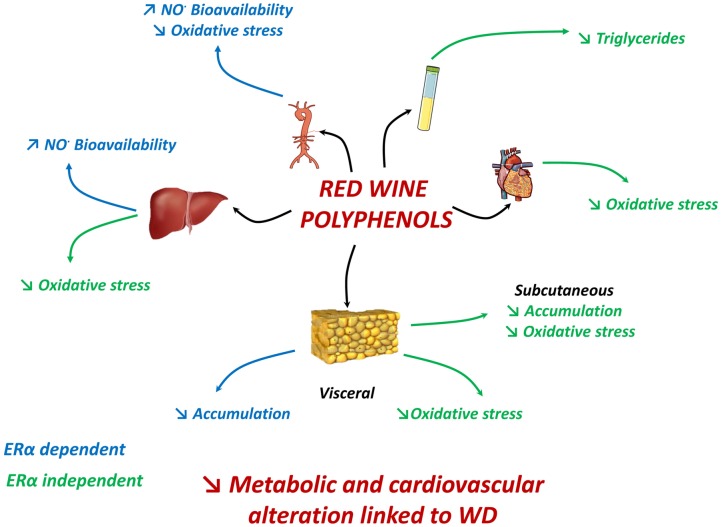
FIGURE 7.
In WD-fed mice, dietary supplementation with polyphenols reduced aortic ROS, enhanced NO• bioavailability in aorta and liver; and reduced visceral adipose tissue accumulation via an ERα-dependent mechanism. Polyphenols decreased plasma triglycerides, subcutaneous fat accumulation and ROS in adipose tissues, liver and heart independent of ERα. Hence, effects generated by polyphenols attenuate most features of metabolic dysfunctions partially via ERα.