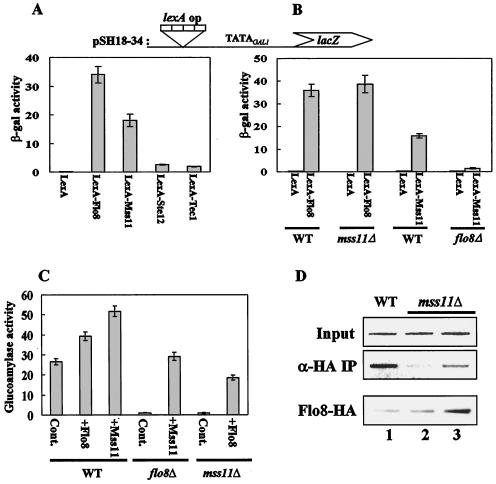
FIG. 3.
Flo8 interacts functionally with Mss11. (A) Transcriptional activation by DNA-bound activators. pSH18-34 (lexA operator) and plasmids expressing LexA-Flo8, LexA-Mss11, LexA-Ste12, LexA-Tec1, or LexA were cotransformed into wild-type (WT) cells grown in synthetic medium lacking uracil and histidine and containing 2% glucose. β-Galactosidase (β-gal) activities were tested on three independent colonies. (B) Activation by LexA-Mss11 requires Flo8. pSH18-34 and the plasmids expressing LexA-Flo8, LexA-Mss11, and LexA were cotransformed into the wild type and the flo8Δ and mss11Δ mutants. β-Galactosidase activities were tested on three independent colonies. (C) Suppression of flo8Δ or mss11Δ mutations by multicopy MSS11 or FLO8, respectively. Empty plasmid pRS326 (control [Cont]), pRS326-FLO8-HA (+Flo8), and pRS326-MSS11-HA (+Mss11) were transformed into the wild type and mutants. The resulting transformants were grown in synthetic medium containing 2% glycerol-ethanol as carbon sources and tested for glucoamylase activity. Glucoamylase activities are averages of the results from three independent experiments. (D) FLO8-HA wild type (lane 1), FLO8-HA mss11Δ (lane 2), and FLO8-HA mss11Δ transformed with pRS326-FLO8-HA (lane 3) were subjected to an anti-HA (α-HA) ChIP assay as described for Fig. 2B with 1 mg of total extracts. The bottom panel represents the level of Flo8-HA in the corresponding strains. The same protein extracts (100 μg) as used in the anti-HA ChIP assay were separated by SDS-8% PAGE and analyzed by Western blot analysis with anti-HA antibody.