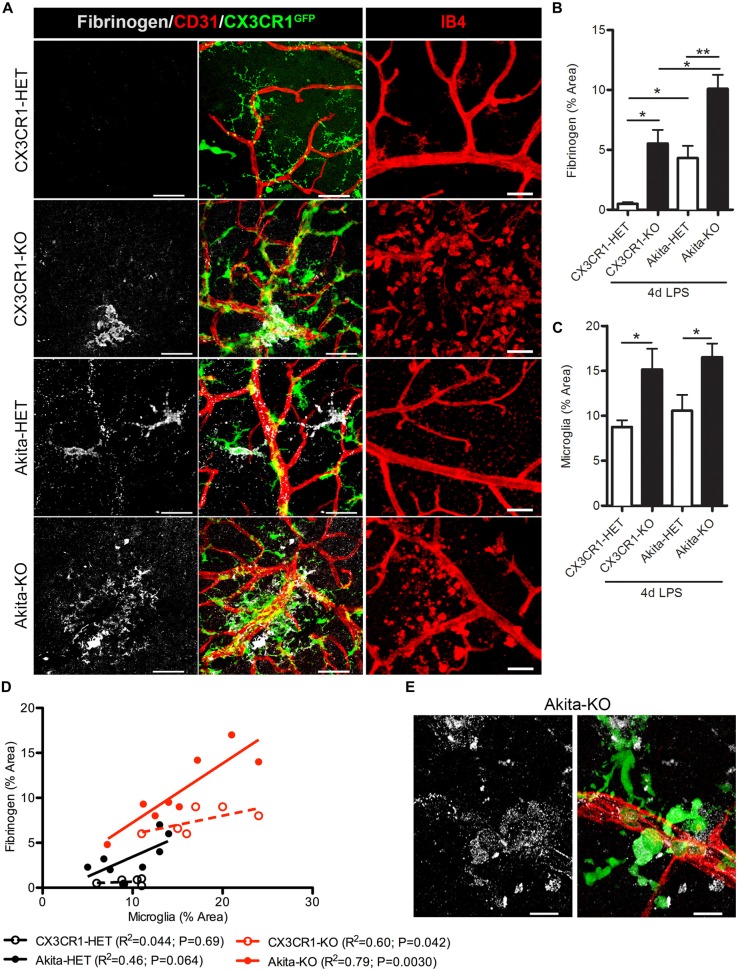
Figure 2.
Endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation triggers fibrinogen accumulation in the diabetic retina and correlates with perivascular microglia clustering in CX3CR1-KO mice. (A) Retinal vascular leakage after systemic inflammation (4 days lipopolysaccharide (LPS)) was assessed by immunostaining for the blood-protein fibrinogen. Fibrinogen deposition (white) around retinal blood vessels (CD31; red) colocalized to microglial lesions (CX3CR1-GFP, green), except in nondiabetic CX3CR1-HET mice (Scale bars: 40 μm). Far right panels show evidence of isolectin B4+ (isolectin b4; IB4, red) cells around disrupted vascular staining in CX3CR1-KO mice (Scale bars: 50 μm). (B) Fibrinogen and (C) microglial CX3CR1-GFP immunoreactivity were quantified per confocal image and data presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4–7 mice per group). *P < 0.05 by ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD (See Table 2 for incidence). (D) Scatter plot analysis of fibrinogen % Area as a function of microglia % Area from data in panels (B,C). (E) Representative high-power confocal image of LPS-treated Akita-KO retina immunostained for fibrinogen (white), microglia (green) and vasculature (CD31, red). Scale bars: 15 μm. **P < 0.01.