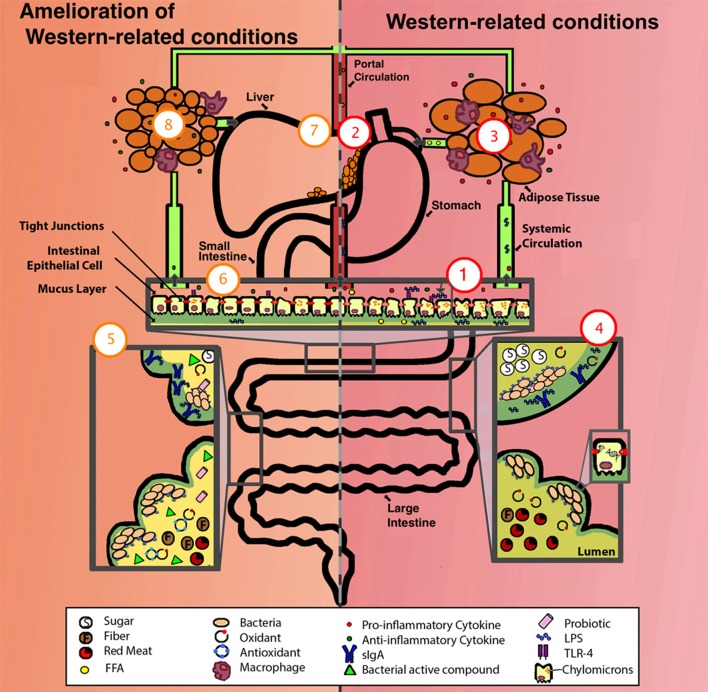
Figure 1.
Comparison of a system suffering from western-related conditions (right, in red) and a system with amelioration of western-related conditions (left, in orange). One aspect of a western lifestyle is the higher intake of ω-6 PUFA (depicted as FFA), this enhances the formation of chylomicrons allowing the translocation of LPS, these then activate basolateral TLR which initiates a pro-inflammatory response, one overall consequence is the alteration of the gut epithelium and its permeability (depicted as deteriorated epithelium and compromised tight junctions), exacerbating inflammation by allowing the translocation of more LPS, pro-inflammatory cytokines, FFA, among other luminal compounds (1). LPS/ pro-inflammatory cytokines/ FFA can enter portal and systemic circulation, one consequence is the alteration of fat metabolism, thus enhancing fat accumulation in liver (2), and in adipose tissue, adipocytes increase in size, FFA synthesis is enhanced (depicted as FFA in circulation), and an elevated pro-inflammatory state occurs (depicted as increased infiltration of macrophages and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines) (3). The western lifestyle includes higher intake of simple sugars and red-meat, lower intake of antioxidants (depicted as presence of oxidants), and sedentarism (depicted as low production of sIgA), some of the consequences are lower-capacity for antigen neutralization (depicted as LPS not bound to sIgA) and damage to the DNA of epithelial cells (depicted as DNA strand breakage) (4). For the amelioration of these conditions, a person can take different approaches, these include exercise (depicted as high production of sIgA), intake of dietary nutrients (i.e., polyphenols and ω-3 PUFAs) (depicted as antioxidants), probiotics, prebiotics, and SCFA (depicted as fiber, bacterial active compounds and probiotics) (5). Some of the effects of these approaches include the reestablishment of gut epithelium permeability and a decrease in LPS translocation, TLR activation, chylomicron formation, presence of LPS/cytokines/FFA in portal and systemic circulation (6), liver fat (7), adipocyte size, FFA synthesis, macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue (8), and an overall amelioration of the inflammatory state (depicted as a higher concentration of anti-inflammatory cytokines compared to pro-inflammatory cytokines [6 and 8]). FFA, free fatty acids. For more details see the text.