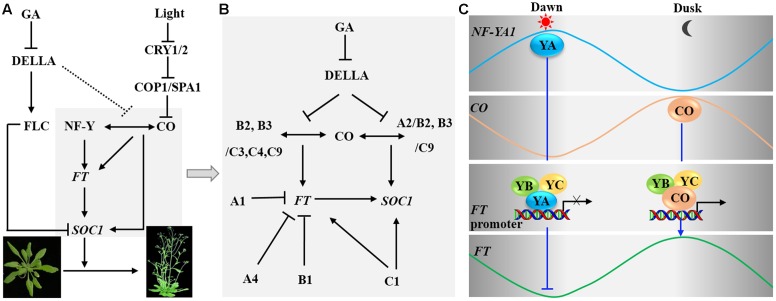
FIGURE 4.
Nuclear factor Y controls flowering time. (A) In the photoperiod pathway, the NF-Y complex can interact with CONSTANS (CO) protein, then binds the promoter region of FT and enhances its transcription. In the gibberellin (GA) signaling pathway, DELLA interacts with FLC and enhances transcriptional repression of FT and SUPPRESOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS1 (SOC1) by FLC. DELLA also represses the interaction of CO with NF-YB2, thus preventing the CO-NF-Y complex from promoting expression of FT and SOC1. (B) A diagram indicating the detailed molecular mechanism is shown in the region in gray in (A). NF-YA1, YA4, and YB1 repress the expression of FT and thus delay flowering; NF-YC1 increases the transcription of FT and SOC1, thus promoting flowering. NF-YB2/B3 and YC3/YC4/YC9 can form a complex with CO and regulate the expression of FT. Moreover, NF-YA2/YB2 and NF-YB3/YC9 interact with CO and regulate the expression of SOC1. (C) CO and NF-Y regulate FT expression. At dawn, NF-YA1-YB-YC form a heterotrimeric complex that binds to the promoter of FT thus repressing its transcription. At dusk, CO competes with NF-YA1 to form a heterotrimeric complex NF-YB-YC-CO to promote the transcription of FT.