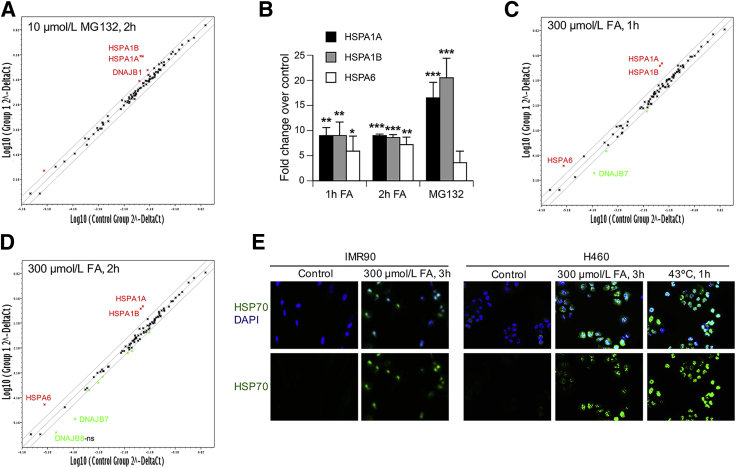
Figure 5.
Gene expression of heat shock proteins and protein chaperones. The gene expression was determined by quantitative RT-PCR using the Human Heat Shock Proteins & Chaperones RT Profiler PCR Array (panels A–D). A: Scatter plot of relative expression for 84 heat shock/protein chaperones-related genes in control and MG132-treated IMR90 cells. Log-transformed values of the relative expression level of each gene (2−ΔCt) between MG132-treated (y axis) and control cells (x axis) are shown. The two-lane corridor indicates a twofold threshold in expression changes. Up-regulated and down-regulated genes by the treatment are indicated by red and green symbols, respectively. B: Expression of HSP70 heat shock genes in MG132-and FA-treated IMR90 cells. C and D: Relative expression for 84 heat shock/protein chaperones-related genes in 1 hour FA-treated (C) and 2 hours FA-treated (D) IMR90 cells. E: Epifluorescence images for protein expression of inducible HSP70 (HSP72/73) in cells treated with FA or subjected to heat shock. Data are expressed as means (A, C, and D) or means ± SD (B). n = 3 experiments (A–D). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 relative to untreated controls. FA, formaldehyde; HSP70, heat shock protein 70; ns, not significant; p-, phosphorylated.