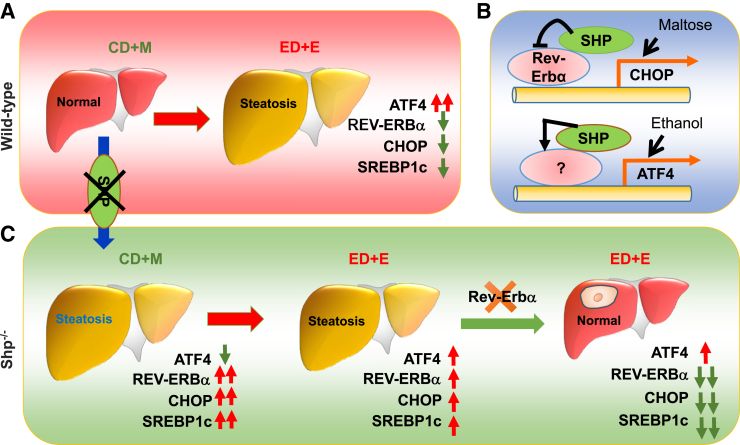
Figure 7.
Schematic summarizing major findings in this study. A: WT mice: ethanol diet + ethanol binge (ED+E) induces steatosis, which correlates with a marked up-regulation of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) protein but down-regulation of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c) protein. However, knockdown ATF4 does not prevent steatosis induced by ED+E. B: Top image: SHP inhibits Chop transcriptional activation by REV-ERBα. Chop induction by loss of SHP repression is augmented by control diet + maltose binge (CD+M). Bottom image: SHP activates ATF4 via an unknown mechanism. ED+E induces ATF4 while transiently down-regulating SHP expression. C:Shp−/− mice: CD+M causes microvesicular steatosis, which correlates with a sharp elevation of CHOP, SREBP-1c, and REV-ERBα protein but a diminished ATF4 protein. On the contrary, ED+E-induced steatosis correlates with moderate up-regulation of ATF4, CHOP, SREBP-1c, and REV-ERBα protein relative to WT-ED+E. Knockdown REV-ERBα prevents ED+E-induced steatosis.