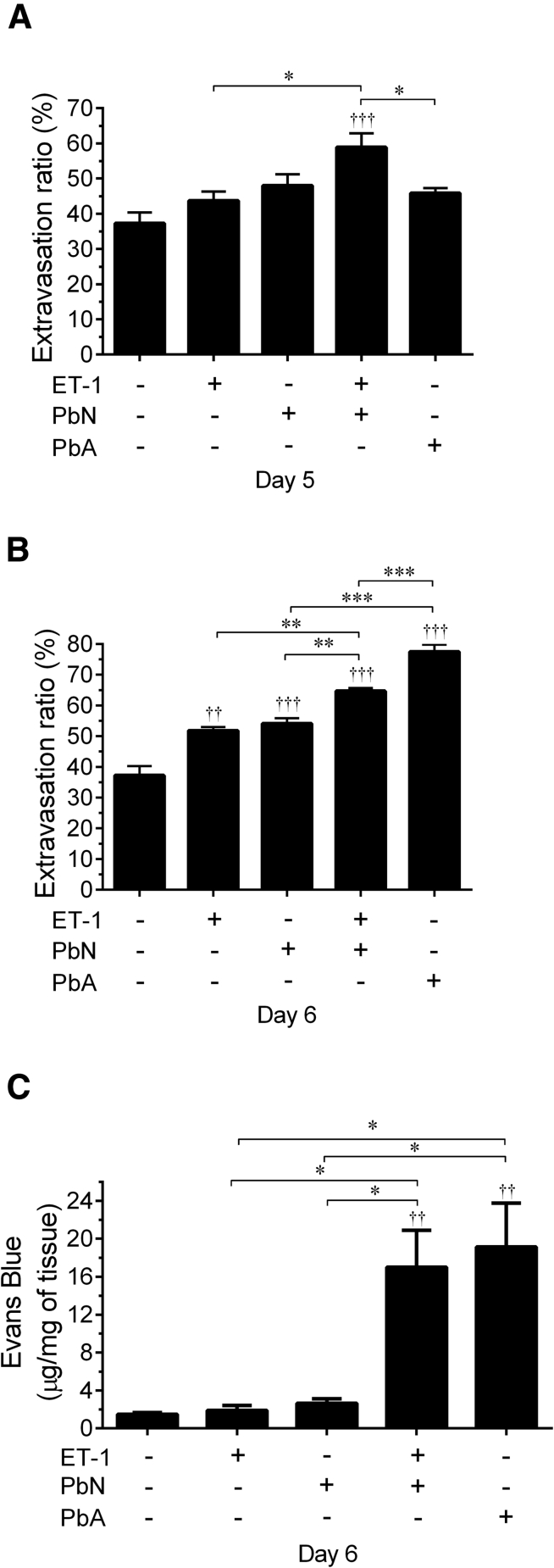
Figure 6.
ET-1 disrupted blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity in PbN-infected mice. A and B: ET-1–treated PbN-infected mice had significantly greater leakage of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) albumin than uninfected mice, using intravital microscopy quantification at 5 and 6 days postinfection (dpi). The degree of BBB leakage was significantly more than in PbA-infected mice. B: At 6 dpi, all infected mice and uninfected mice treated with ET-1 had significantly more leakage of FITC albumin than uninfected mice given normal saline (NS). The leakage of FITC albumin was significantly greater in PbN-infected mice treated with ET-1 than PbN-infected mice given NS or uninfected mice treated with ET-1. PbA-infected mice had significantly more FITC albumin leakage than PbN mice, with or without ET-1 treatment. C: With Evans Blue Dye (EBD) bound albumin quantification, PbA-infected and PbN + ET-1 mice had significant BBB disruption compared to uninfected mice given NS, whereas PbN mice and uninfected mice treated with ET-1 had similar levels of EBD leakage in the brain to uninfected mice given NS. The EBD leakage in PbA-infected and in ET-1–treated PbN-infected mice was significantly greater than either PbN mice treated with NS or ET-1–treated uninfected mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 when comparing groups; ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001 relative to baseline measurements.