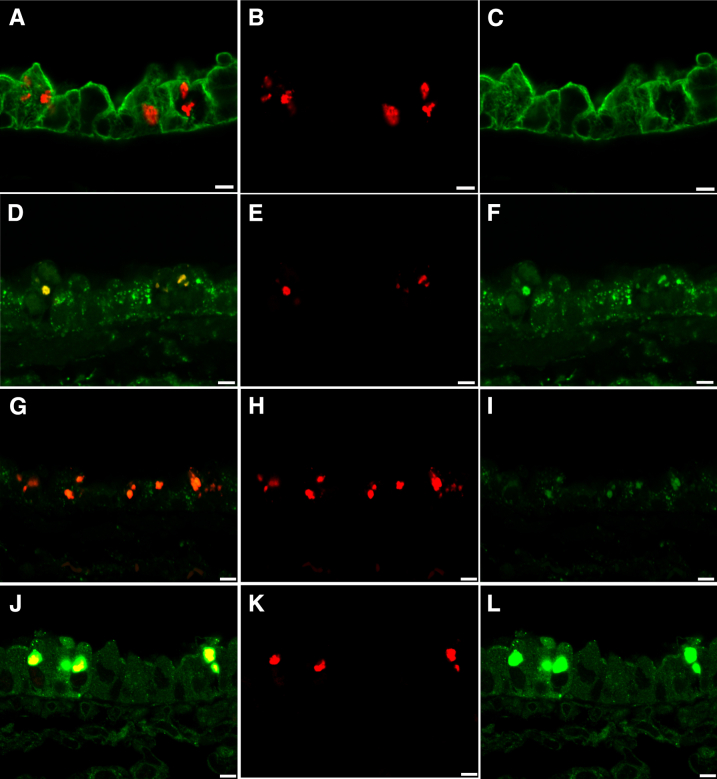
Figure 5.
Ubiquitin puncta were localized to endosomal/lysosomal/exosomal vesicles and SQSTM1 puncta using confocal microscopy of immunofluorescence staining for ubiquitin (red), cytoskeletal components KRT8 and KRT18 (green, A–C), endosomal/lysosomal/exosomal marker LAMP1 (green, D–F), endosomal/lysosomal/exosomal marker LAMP2 (green, G–I), and the multifunctional scaffolding protein SQSTM1 (green, J–L) in the airway epithelium of diacetyl-exposed mice. A: In this merged image, ubiquitin appears red because it is in spaces between the cytoskeletal filaments (green). B: Ubiquitin in the section shown in A. C: The cytoskeletal intermediate filaments containing cytoskeletal components KRT8 or KRT18 (green) in A are distinct from the sites where ubiquitin is observed in B. D: In this merged image, the yellow demonstrates colocalization of ubiquitin (red) with the endosomal/lysosomal/exosomal marker LAMP1 (green). E: Ubiquitin (red) in the section shown in D. F: LAMP1 (green) in the section shown in D is present in the sites where uibiquitin is observed in E. G: In this merged image, the orange demonstrates colocalization of ubiquitin (red) with the endosomal/lysosomal/exosomal marker LAMP2 (green, G–I). H: Ubiquitin (red) in the section shown in G. I: LAMP2 (green) in the section shown in G is present in most areas where ubiquitin is present. J: In this merged image, ubiquitin (red) is associated with SQSTM1 (green, J–L), resulting in yellow within the sites containing the green puncta of the scaffolding protein, SQSTM1. K: Ubiquitin (red) in the section shown in J. L: SQSTM1 (green) in the section shown in J is present in the sites of cellular ubiquitin accumulation. Scale bar = 5 μm (A–L).