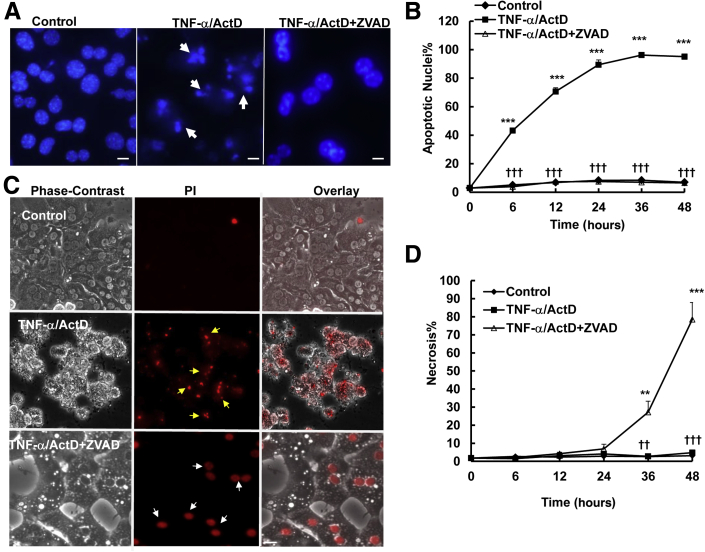
Figure 1.
Inhibition of caspase by ZVAD switches TNF-α/ActD-induced apoptosis to necrosis in cultured hepatocytes. Primary mouse hepatocytes were either untreated (control) or treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α plus 0.1 μg/mL ActD, 50 μmol/L TNF-α/ActD plus ZVAD. A: Hepatocytes were treated as described above for 6 hours and stained with 1 μg/mL Hoechst 33342, followed by fluorescence microscopy. Representative images of hepatocyte nuclei are shown. Arrows denote apoptotic fragmented nuclei. B: Quantification of apoptotic nuclei after the cells were treated as described for different time points. C: Hepatocytes were treated as in panel A for 24 hours and stained with 1 μg/mL PI, followed by fluorescence microscopy. Representative phase-contrast, PI, and overlaid hepatocyte images are shown. Yellow arrows denote the fragmented PI-positive nuclei (secondary necrosis), and white arrows denote the PI-positive intact nuclei (necrosis). D: Quantification of necrosis after the cells were treated as described for different time points. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments, and more than 100 cells counted in each experiment. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus control; ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001 versus TNF-α/ActD. One-way analysis of variance analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. Scale bar: 20 μm (A and C). ActD, actinomycin D; PI, propidium iodide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.