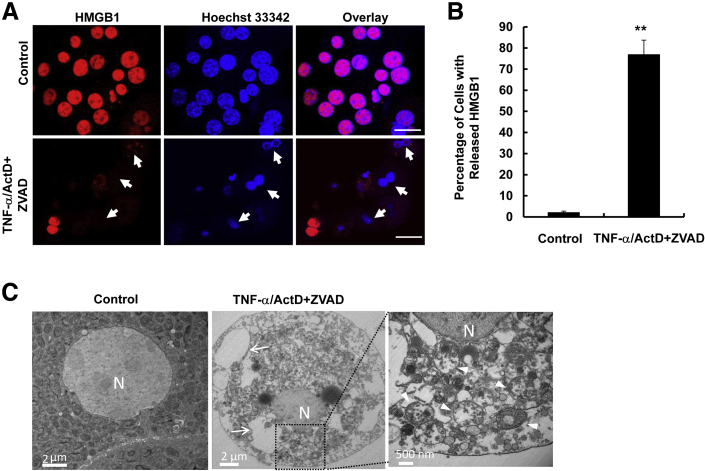
Figure 2.
TNF-α/ActD+ZVAD treatment induces HMGB1 nuclear release and disruption of cellular organelles. Primary mouse hepatocytes were either untreated (control) or treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α + 0.1 μg/mL ActD + 50 μmol/L ZVAD for 48 hours. A: Hepatocytes were fixed and immunostained for HMGB1 and treated as described above for 6 hours and stained with 1 μg/mL Hoechst 33342, followed by fluorescence microscopy. Representative images of hepatocyte nuclei are shown. Arrows denote apoptotic fragmented nuclei. B: Quantification of apoptotic nuclei after the cells were treated as described for different time points. C: Cells were treated as in panel A for 48 hours and further processed for EM analysis. Representative EM images are shown. Right panel is an enlarged image from boxed area. Arrows indicate large cellular vacuoles; arrowheads, damaged mitochondria. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments, and more than 100 cells counted in each experiment. ∗∗P < 0.01 versus control. One-way analysis of variance analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. Scale bars: = 20 μm (A); 2 μm (C, left and center panels); 500 nm (C, right panel). ActD, actinomycin D; EM, electron microscopy; HMGB, high mobility group box 1 protein; N, nucleus; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.