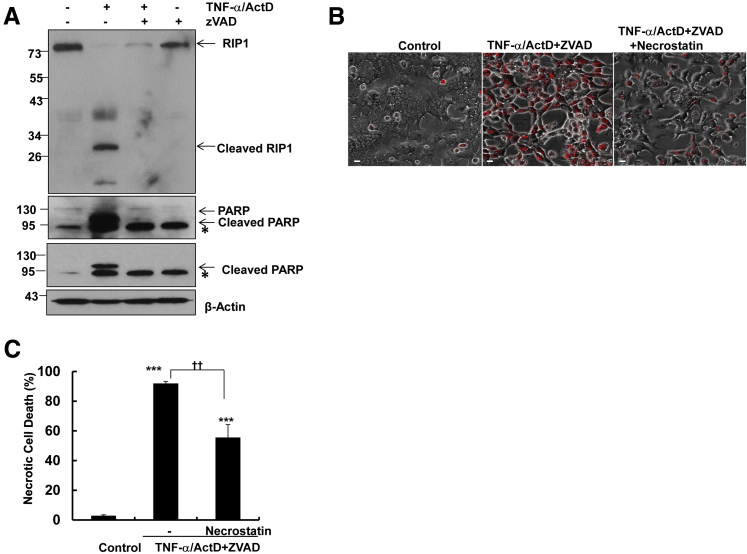
Figure 6.
TNF-α/ActD+ZVAD-induced necrosis is partially inhibited by necrostatin in hepatocytes. A: Primary mouse hepatocytes were either untreated (control) or treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α + 0.1 μg/mL ActD in the presence or absence of 50 μmol/L ZVAD for 6 hours, and total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. All of the gels have been run under the same experimental conditions. Asterisks indicate no specific band. B: Primary mouse hepatocytes were either untreated (control) or treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α + 0.1 μg/mL ActD + 50 μmol/L ZVAD in the presence or absence of 40 μmol/L necrostatin for 48 hours. Representative phase-contrast and PI staining overlaid images of hepatocytes are shown. C: Quantification of the PI-positive necrotic cells. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments, and more than 100 cells counted in each experiment. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus control; ††P < 0.01 versus TNF-α/ActD+ZVAD. One-way analysis of variance analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. Scale bar = 20 μm (B). ActD, actinomycin D; PI, propidium iodide; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; RIP, receptor-interacting protein kinase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.