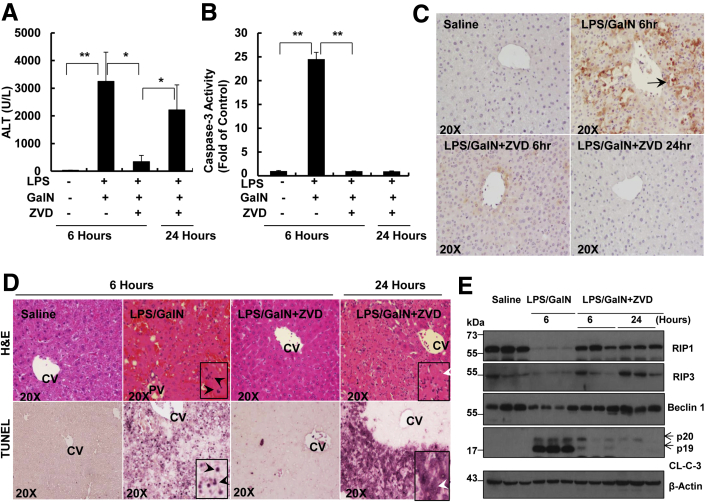
Figure 7.
Inhibition of caspase protects against LPS/GalN-induced liver injury during the early phase but induces necrotic cell death during the late phase. A: WT male C57Bl/6 mice were treated with 700 mg/kg GalN i.p. and 100 μg/kg LPS i.p. for 6 hours. For the ZVD experiments, after the mice were given LPS/GalN for 3 hours, mice were further given 10 mg/kg ZVD i.p. for another 3 hours or 21 hours. All of the mice were sacrificed at 6 or 24 hours after the administration of LPS/GalN. A: Serum ALT values were determined and B: Total liver lysates were subjected to caspase-3 activity assay. C: Representative images of liver tissues that were immunostained with a cleaved caspase-3 antibody. Arrows denote cleaved caspase-3–positive cells. D: Representative images of liver tissue H&E staining and TUNEL staining. Black arrowheads denote apoptotic nuclei. White arrowheads denote necrotic cells. E: Total liver lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. All of the gels were run under the same experimental conditions. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 to 7 mice per group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. One-way analysis of variance analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. Original magnification: ×20 (C and D, main images); ×40 (D, insets). ALT, alanine aminotransferase; CL-C-3, cleaved caspase-3; CV, central vein; GalN, D-galactosamine; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PV, portal vein; RIP, receptor-interacting protein kinase; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; WT, wild-type; ZVD, N-benzyloxycabonyl-Val Asp-fluoromethyl ketone.