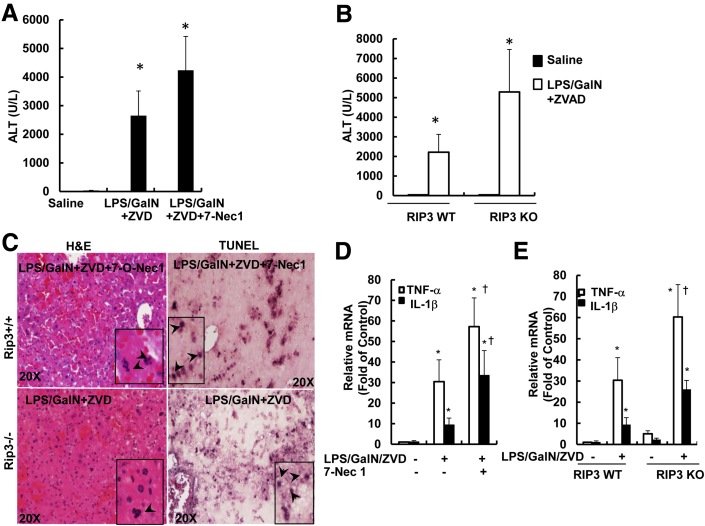
Figure 8.
Pharmacologic inhibition of RIP1 or genetic deletion of RIP3 does not protect against LPS/GalN/ZVD-induced late-phase liver injury. A: WT male C57Bl/6 mice were treated with 700 mg/kg GalN i.p. and 100 μg/kg LPS i.p. for 6 hours. After the mice were given LPS/GalN for 3 hours, mice were further treated with 10 mg/kg ZVD i.p. for another 21 hours or co-injected with 10 mg/kg 7-Nec1. All of the mice were sacrificed at 24 hours after the administration of LPS/GalN. A: Serum ALT values were determined. B: WT and RIP3 KO mice were given LPS/GalN for 3 hours, and the mice were further treated with 10 mg/kg ZVD i.p. for another 21 hours. All of the mice were sacrificed at 24 hours after the administration of LPS/GalN. B: Serum ALT values were determined. C: Representative images of liver tissue H&E staining and TUNEL staining. Arrows denote apoptotic nuclei. D and E: Mice were treated as in panels A and B; RNA was extracted from mouse livers and used to measure gene expression by qPCR. Results were normalized to β-actin and expressed as fold-change compared with control. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 to 7 mice per group (A and B); n = 4 to 5 mice per group (D and E). ∗P < 0.05 versus control; †P < 0.05 versus LPS/GalN/ZVD. One-way analysis of variance analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. Original magnification: ×20 (C, main images); ×40 (C, insets). ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GalN, D-galactosamine; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; KO, knockout; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; qPCR, real-time quantitative PCR; RIP, receptor-interacting protein kinase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; WT, wild-type; ZVD, N-benzyloxycabonyl-Val Asp-fluoromethyl ketone; 7-Nec1, 7-Cl-O-Nec-1.