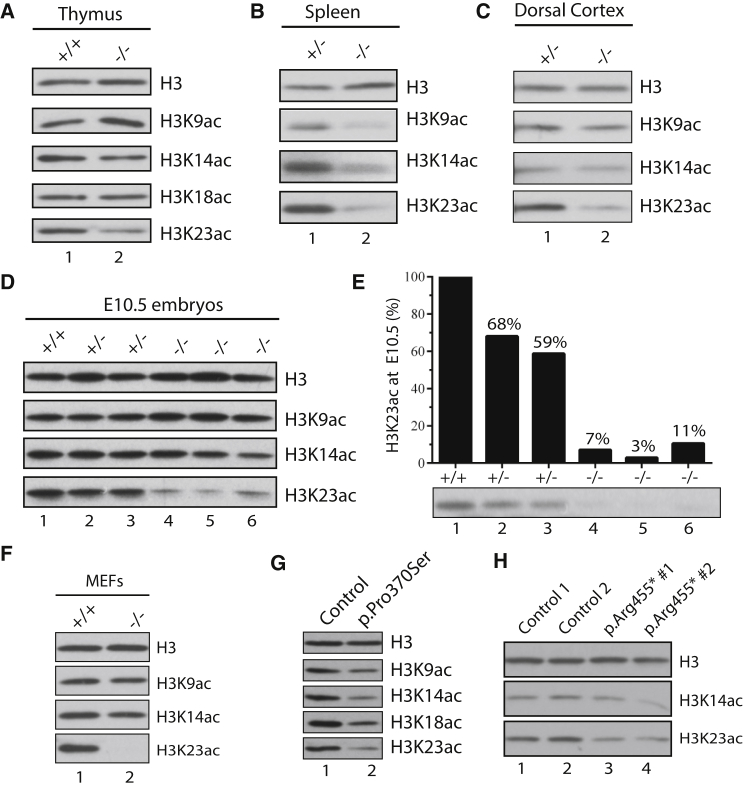
Figure 3.
BRPF1 Loss Reduces Histone H3K23 Acetylation In Vivo
(A and B) Histone H3 acetylation in thymus and spleen protein extracts from control and hematopoietic-specific Brpf1-knockout mice.
(C) Histone H3 acetylation in dorsal cortical extracts from heterozygous and forebrain-specific Brpf1 knockouts.
(D) Histone H3 acetylation in protein extracts from wild-type and epiblast-specific Brpf1-knockout embryos at embryonic day 10.5 (E10.5).
(E) Quantification of H3K23 acetylation in proteins extracts from wild-type and epiblast-specific Brpf1 knockout embryos at E10.5. The blot was from the same experiment as shown in (D), but the exposure time was shorter than the bottom image in (D). The quantification was performed with NIH ImageJ.
(F) Histone H3 acetylation in protein extracts from control and Brpf1-knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). The fibroblasts were prepared from control and tamoxifen-inducible knockout embryos at E15.5.27
(G) Histone H3 acetylation in protein extracts from control and p.Pro370Ser lymphoblastoid cells.
(H) Histone H3 acetylation in protein extracts from control and p.Arg455∗ fibroblasts.