Figure 2.
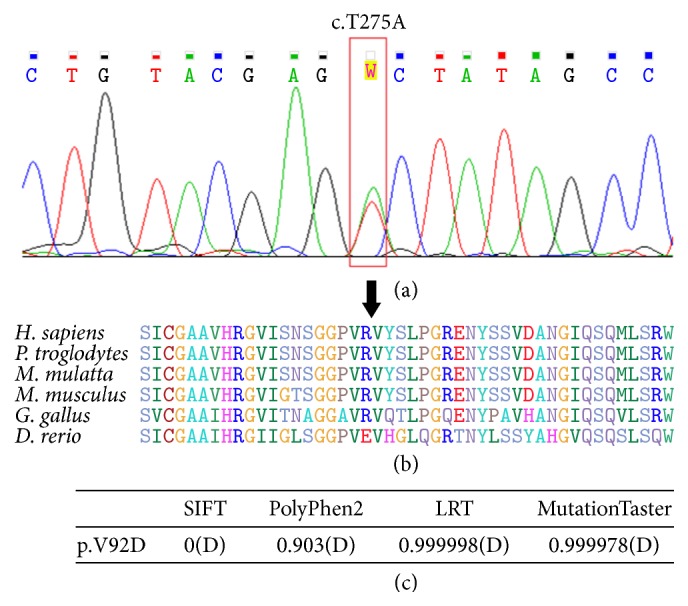
(a) Sanger sequencing chromatograms showing the c.T275A p.V92D mutation of the family. (b) Protein sequence alignment showing conservation of the V92 residue in cochlin across human (H. sapiens), chimpanzee (P. troglodytes), macaca (M. mulatta), mouse (M. musculus), chicken (G. gallus), and zebrafish (D. rerio). (c) Pathogenicity prediction using computational programs. D in the parentheses stands for deleterious.
