Fig. 2.
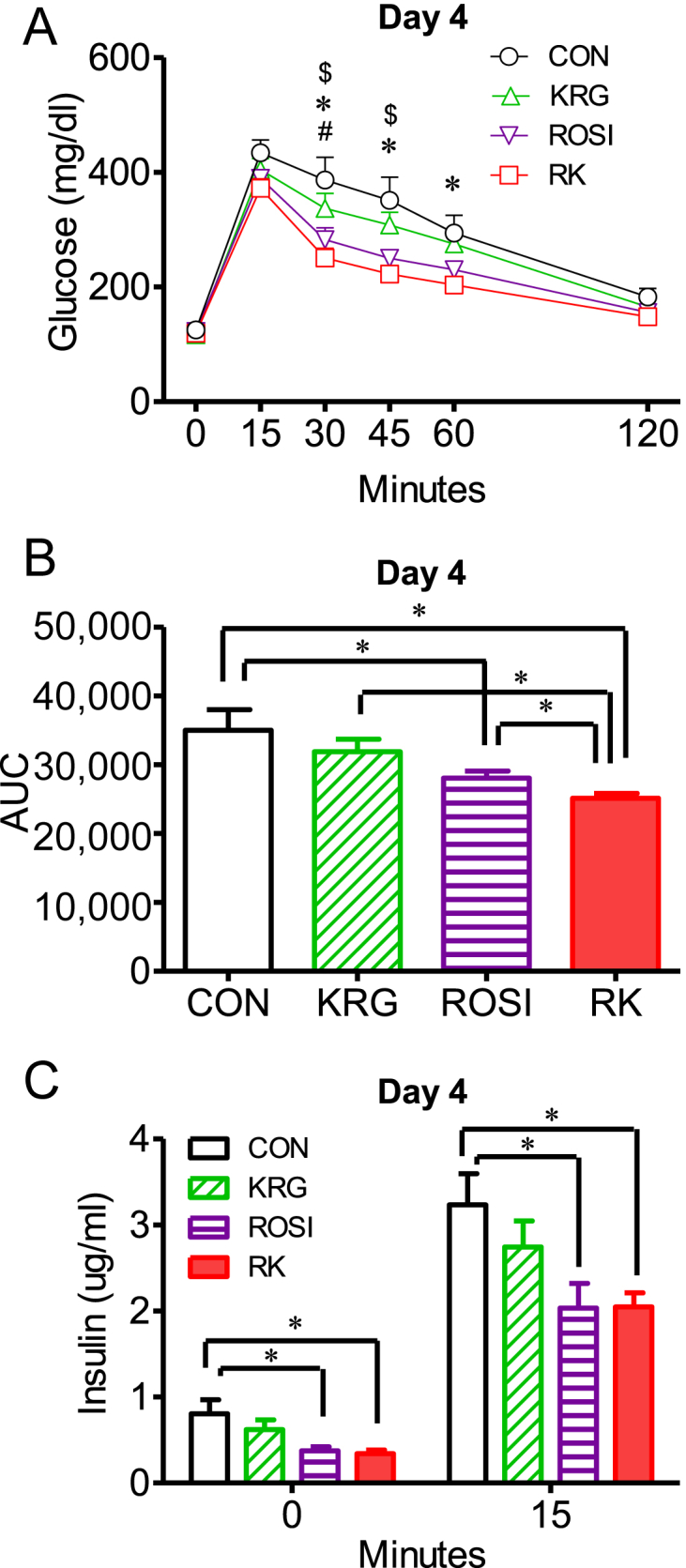
The effect of rosiglitazone combined with Korean Red Ginseng on glucose tolerance and serum insulin in diet-induced obese mice. (A) Oral glucose tolerance tests (oGTTs) were performed after 4 days of treatment with ROSI and KRG in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. (B) Comparison of the area under the glucose curve (AUC). (C) Serum insulin levels at 0 minutes and 15 minutes after the glucose load during the oGTTs. Data are presented as the mean ± the standard error of the mean. $p < 0.05, CON versus ROSI. & p < 0.05, ROSI versus KRG. # p < 0.05, KRG versus RK. * p < 0.05, CON versus RK. ∗ p < 0.05; AUC, area under the glucose curve. CON, study group treated with 0.5% methyl cellulose and 0.9% saline; KRG, study group treated with 500 mg/kg body weight (b.w.) of Korean Red Ginseng; RK, study group treated with 500 mg/kg b.w. KRG combined with 15 mg/kg b.w. rosiglitazone; ROSI, study group treated with 15 mg/kg b.w. of rosiglitazone.
