Fig. 1.
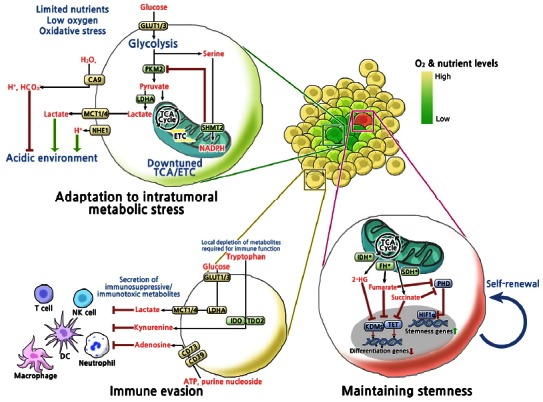
Overview of metabolic mechanisms involved in adaptation to intratumoral metabolic stress, maintaining stemness and immune evasion. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells enhances fitness toward intratumoral metabolic stress and immune surveillance, and contributes to maintaining stemness. GLUT1/3, Glucose transporter 1/3; PKM2, M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase; SHMT2, Serine hydroxymethyltransferase; LDHA, Lactate dehydrogenase A; NHE1, Na+/H+-exchanger; MCT1/4, Monocarboxylate transporters; CA9, Carbonic anhydrase 9; IDH*, Gain-of-function mutation in isocitrate dehydrogenase1/2; FH*, Loss-of-function mutation in fumarate hydratase; SDH*, Loss-of-function mutation in succinate dehydrogenase; PHD, Prolyl hydroxylases; HIF1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; KDMs, Histone lysine demethylases; TET, Ten eleven translocation family of 5-methylcytosine (3mC) hydroxylases; IDO1, Indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase 1; TDO2, tryptophan-2, 3-dioxygenase 2; CD73, Ecto-5′-nucleotidases; CD39, Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1.
