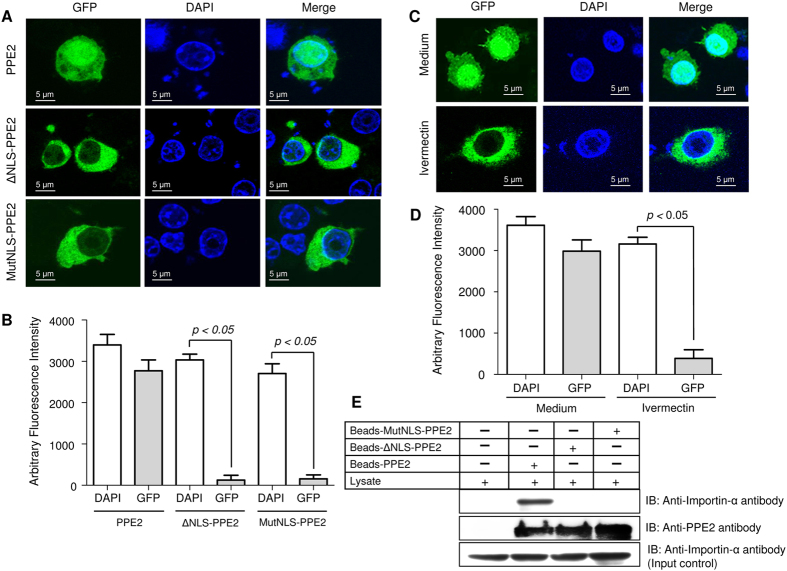
Figure 1. PPE2 contains a functional nuclear localization signal.
(A) EGFP-tagged PPE2 protein (green) with mutated NLS failed to translocate into the nucleus. RAW 264.7 macrophages were transfected with either EGFP-tagged wild-type PPE2 (EGFP-PPE2) or PPE2 with truncated NLS (EGFP-ΔNLS-PPE2) or PPE2 with mutated NLS (EGFP-MutNLS-PPE2) and examined by confocal microscopy after at 24 hours post-transfection. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Blue). (B) Image quantification of nuclear import of PPE2 was carried out in cells (n = 24) transfected with EGFP-tagged either wild-type PPE2 (EGFP-PPE2) or PPE2 with truncated NLS (EGFP-ΔNLS-PPE2) or PPE2 with mutated NLS (EGFP-MutNLS-PPE2) using ImageJ software. (C) EGFP-tagged PPE2 failed to be translocated to the nucleus in the presence of ivermectin, a classical nuclear import inhibitor. RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with EGFP-PPE2 (green) followed by treatment with 10 μM ivermectin or vehicle controls and examined under a confocal microscope at 24 hours post-transfection. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Blue). (D) Image quantification of nuclear import of PPE2 in RAW 264.7 macrophages was carried out using ImageJ software. Twenty cells per experimental sample were taken for quantification of nuclear import of PPE2 in RAW 264.7 macrophages. (E) The NLS of PPE2 interacts with importin-α. Talon-bound 6X-histidine-tagged wild-type PPE2, MutNLS-PPE2 and ΔNLS-PPE2 were incubated with RAW 264.7 lysates overnight and after washing, the bound proteins were probed by Western blotting using anti-importin-α antibody or anti-PPE2 antibody. About 50 μg of the cell extract from each group was used as input control. All data are representative of 3 independent experiments.