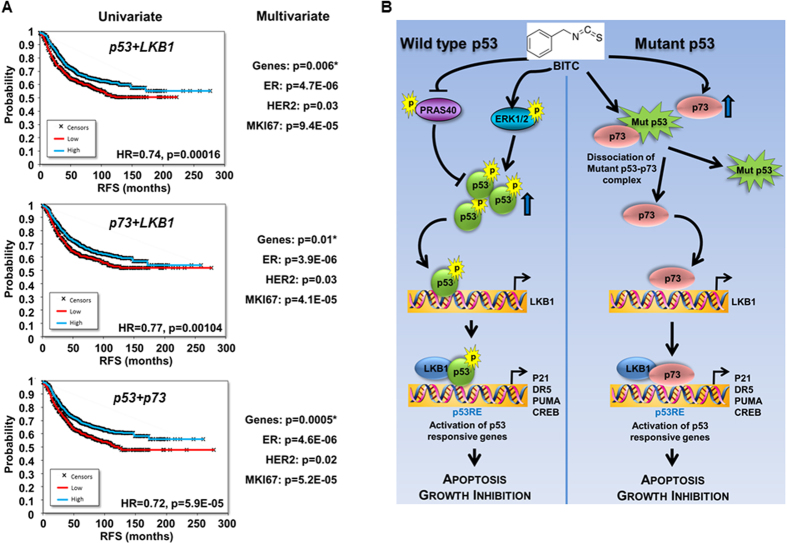
Figure 7. Survival analyses of p53, p73 and LKB1 and schematic representation of BITC-mediated crosstalk between p53, LKB1 and p73.
(A) Survival analyses in 1,819 patients for TP53+LKB1, TP73+LKB1, and for TP53+TP73. Univariate analysis was performed using the combination of the two genes in patients with relapse-free survival data. Multivariate regression analysis involving estrogen receptor and HER2 receptor status and MKI67 expression. (B) BITC treatment inhibits PRAS40 and induces phosphorylation of ERK leading to increased phosphorylation and accumulation of p53. BITC also induces recruitment of p53 to p53-response element (p53RE) on LKB1 promoter leading to increased LKB1 expression which in turn forms a complex with p53 and gets recruited to p53RE on p53-responsive genes. In p53-mutant breast cancer cells, BITC increases p73 expression as well as abrogates the complex between mutant-p53 and p73 hence freeing p73 and stimulates p73 recruitment to p53RE on LKB1 promoter. LKB1 and p73 tether and get recruited to p53-responsive genes in the presence of BITC. BITC induces apoptosis and inhibits growth of p53-wild-type as well as p53-mutant breast cancer cells via mediating crosstalk between p53, LKB1 and p73.