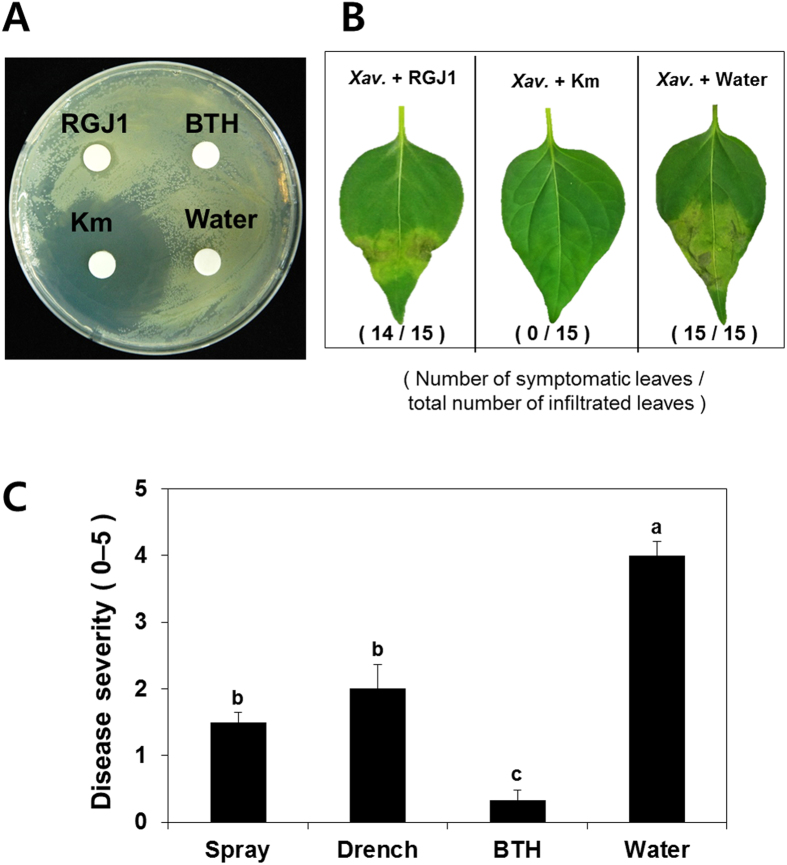
Figure 3. Validation of induced resistance.
(A) No antagonism displayed between strain RGJ1 and the pathogen X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria. The photo was taken 2 days after inoculation of 20 μL of strain RGJ1 at 108 cfu/mL, 25 μg/mL kanamycin, 20 μL of 1 mM BTH, and water control on a lawn of X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria. (B) In-plant assay to validate direct antagonism by strain RGJ1. Xav = X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria; RGJ1 = Pseudozyma churashimaensis strain RGJ1; Km = kanamycin The disease symptoms were investigated 7 days after leaf infiltration with three treatments: (1) 1:1 mixture of strain RGJ1 and X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria; (2) 1:1 mixture of strain RGJ1 and 25 μg/mL kanamycin; (3) 1:1 mixture of strain RGJ1 and sterile distilled water. (C) Comparison between the different inoculation methods. Strain RGJ1 (108 cfu/mL) was sprayed on leaf or drenched on root. Disease severity was measured 1 week after leaf infiltration of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria at OD = 0.001. Bars represent the mean ± SE (sample size, N = 10 replications per treatment). Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P = 0.05 according to least significant difference).