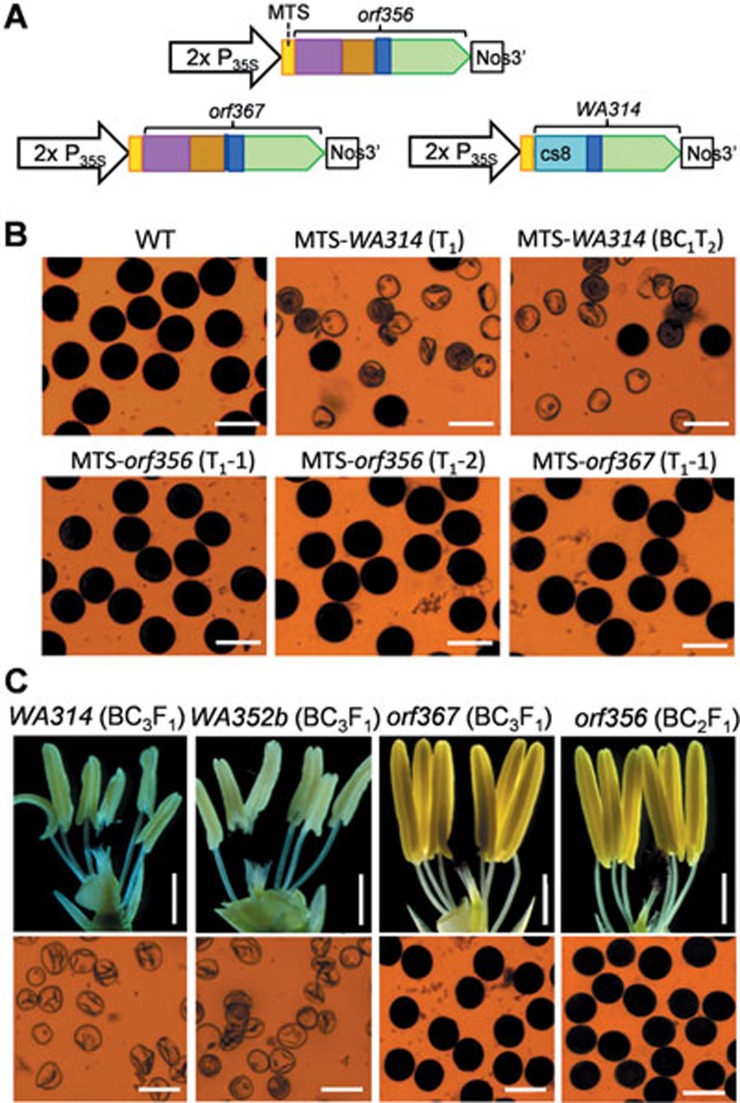
Figure 2.
Functional analysis of the putative CMS genes. (A) Binary constructs for testing CMS function of the putative CMS genes by nuclear transformation (2× P35S, doubled CaMV35S promoter; MTS, sequence encoding a mitochondrial transit signal; Nos3′, transcriptional termination sequence). (B) Pollen phenotype of the rice plants carrying the transgenes. The BC1T1 plants with MTS-WA314 were obtained by backcrossing with ZS97B. WT is a negative segregant without the transgene (MTS-WA314) selected from a T1 family. The transgenic plants carrying MTS-WA314 exhibited partial male sterility (deflated pollen grains), but those with MTS-orf356 and MTS-orf367 produced fertile pollen. Pollen grains were stained with 1% potassium iodide. Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Anther (top) and pollen (bottom) phenotypes of the backcrossed plants with ZS97B as the recurrent parent and wild rice accessions containing the putative CMS genes as cytoplasm donors. The plants with WA314 and WA352b showed aberrant (pale-white) anthers with sterile pollen. Scale bars, 1 mm for anthers and 50 μm for pollen.