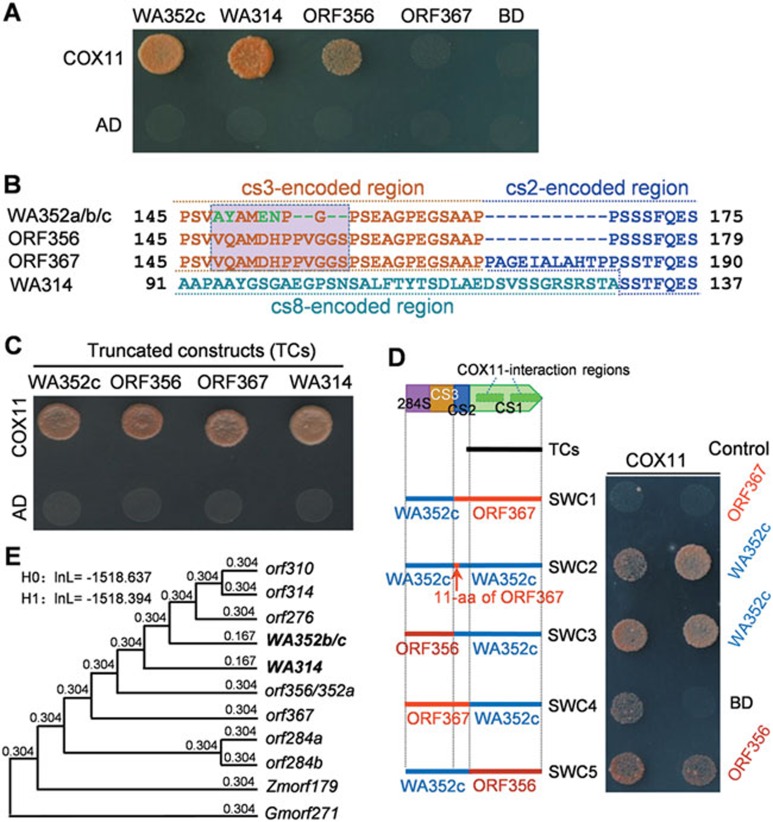
Figure 6.
Functionalization and natural selection of the CMS-related genes. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assays of the interaction of WA352c, ORF356, ORF367, and WA314 (in pGBKT7 vector, BD) with COX11 (in pGADT7, AD). The yeast cells were grown on SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade medium. (B) The aa changes (in green) and the 11-aa deletion in WA352a, WA352b, and WA352c, and the replacement of the cs3-encoded sequence in WA314. These variations release the interaction potential with COX11. (C) Yeast two-hybrid assays of the COX11-interaction of four truncated constructs (169 aa in length) as shown in (D). (D) Test of the swapped constructs (SWC1-SWC5) and the controls for the interaction with COX11. (E) Estimation of non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rate ratios (dN/dS) of the cs1 sequences in the ORFs using the one-ratio model (for the null hypothesis H0) and the branch model (for the alternative hypothesis H1) of the PAML/CODEML program. H0 assumes that all the cs1 branches in the phylogenetic tree have the same evolutionary rate; H1 assumes that the branch cs1 sequences of the functional WA352b/c and WA314 have a different evolutionary rate from the others. No significant difference (P > 0.05) of the log likelihoods (InL) was detected between H0 and H1. The cs1 sequences of Zmorf179 and Gmorf271 are from maize and soybean, respectively.