Fig. 2.
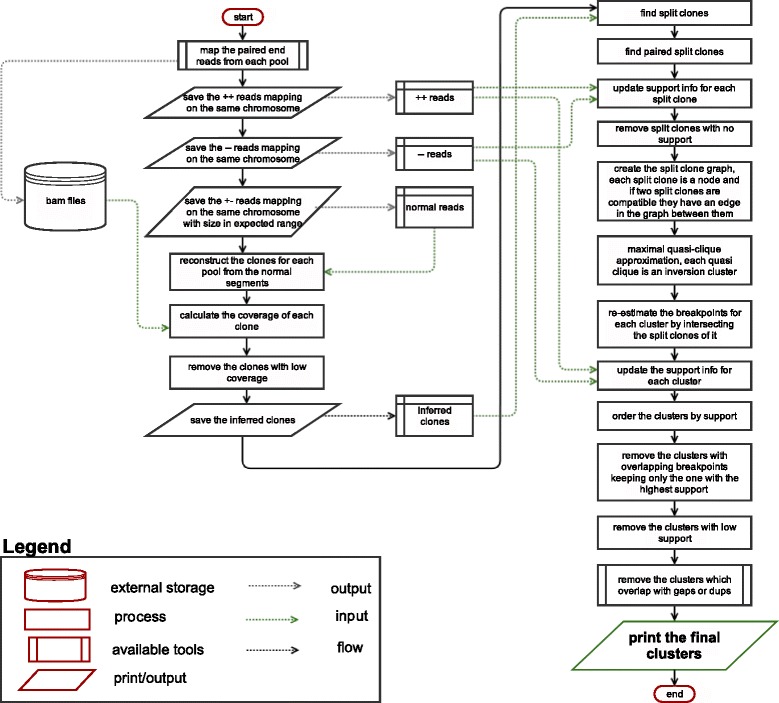
The Valor algorithm. We start with mapping paired-end reads for each pool. We then separate read pairs that map to the same strand, and generate two files for the two strands. We use the concordantly mapping reads to reconstruct clone locations, and calculate depth and breadth of coverage for the clones. Next, we remove clones with low coverage values, which results in the inferred clone locations. We identify the split clones from this list, and then find PSC, then we remove those with insufficient read pair support. Remaining PSCs are used to construct a graph, which we then use to find maximal quasi cliques that signal possible inversion locations. The clone and read pair support are then recalculated for the merged PSCs, those with low support and those that intersect with reference assembly gaps, or intersect with segmental duplications in both breakpoints are discarded
