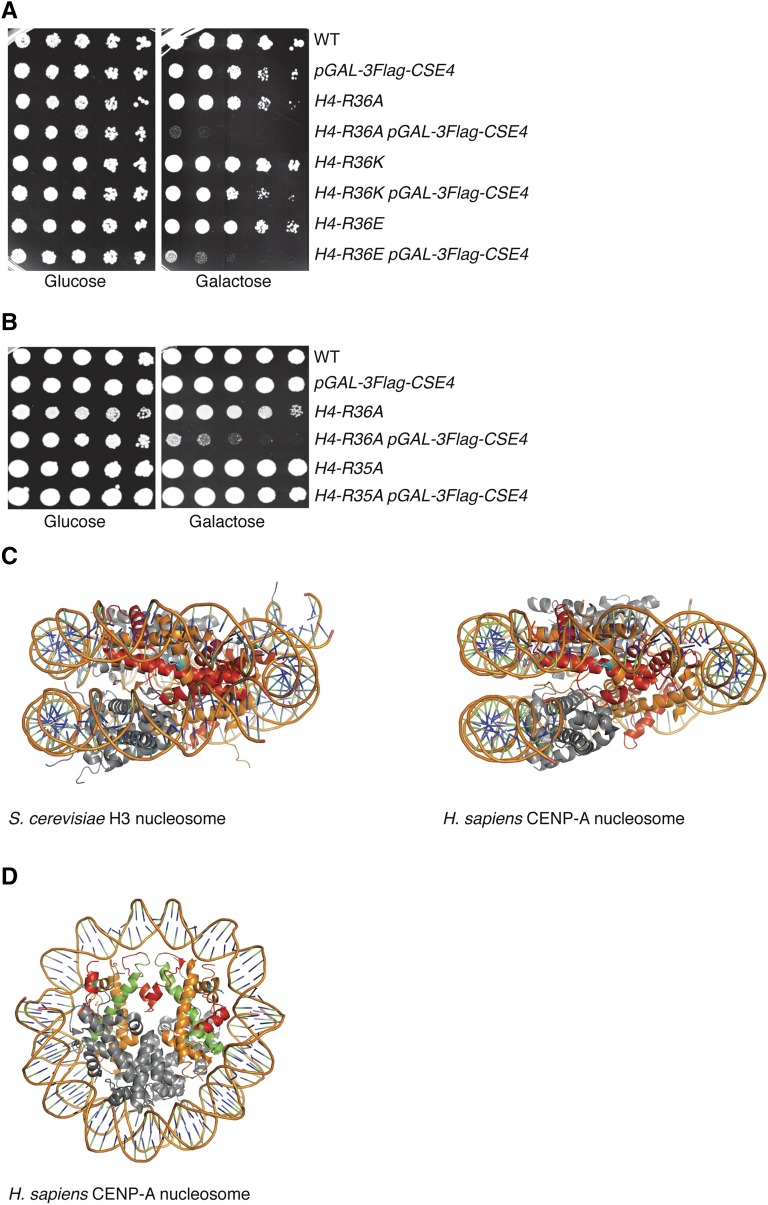
Figure 1.
CENP-ACse4 overexpression is lethal to H4-R36A cells. (A) Fivefold serial dilutions of the indicated strains [WT (SBY13389), pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY13390), H4-R36A (SBY13391), H4-R36A pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY13392), H4-R36K (SBY13393), H4-R36K pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY13394), H4-R36E (SBY13395), and H4-R36E pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY13396)] were plated on glucose or galactose media at 23°. (B) Fivefold dilutions of the indicated strains [WT (SBY9401), pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY10025), H4-R36A (SBY9365), H4-R36A pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY9397), H4-R35A (SBY10510), and H4-R35A pGAL-3Flag-CSE4 (SBY13407)] were plated on glucose or galactose media at 23°. (C) Side views of crystal structures of the S. cerevisiae nucleosome containing histone H3 (left) and the Homo sapiens nucleosome containing CENP-A (right). Histone H4 (orange) residue R36 (cyan) makes side-chain interactions with nucleosomal DNA. Red: histone H3 (left) or CENP-A (right). (D) Top view of the crystal structure of the H. sapiens nucleosome containing CENP-A as in (C), with the CATD indicated (green). WT, wild-type.