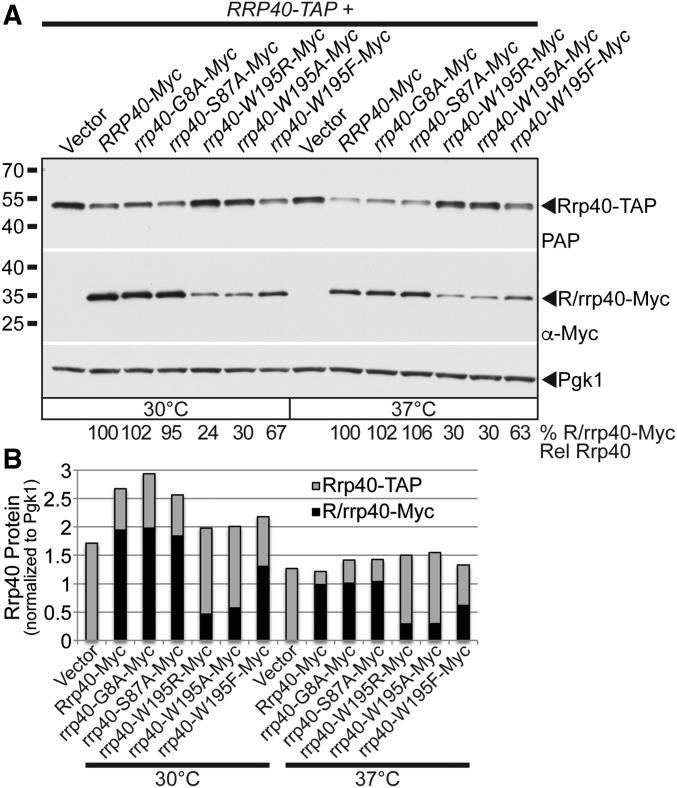
Figure 5.
In an in vivo competition experiment, the rrp40-W195R-Myc variant is present at a greatly reduced level relative to wild-type Rrp40-Myc in cells coexpressing wild-type Rrp40-TAP. (A) rrp40-W195R-Myc and rrp40-W195A variants are expressed at lower steady-state levels compared to Rrp40-Myc in RRP40-TAP cells at 30 and 37°. Lysates of RRP40-TAP cells expressing wild-type Rrp40-Myc, or variant rrp40-Myc (G8A, S87A, W195R, W195A, and W195F) grown at 30 or 37° were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-tagged Rrp40 and rrp40 variants (R/rrp40-Myc), PAP antibody to detect Rrp40-TAP, and anti-Pgk1 antibody to detect Pgk1 as a loading control. The percentage of Rrp40-Myc and rrp40-Myc variant relative to wild-type Rrp40-Myc (% R/rrp40-Myc Rel Rrp40) is shown below each lane, and was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The immunoblot in (A) was quantitated to graph the relative intensity of wild-type Rrp40-Myc, variant rrp40-Myc, Rrp40-TAP protein bands in cells coexpressing R/rrp40-Myc and Rrp40-TAP at 30 and 37°. Cells with low levels of rrp40-W195R-Myc or rrp40-W195A-Myc variant have high levels of Rrp40-TAP. Cells with high levels of rrp40-G8A-Myc or rrp40-S87A variant have low levels of Rrp40-TAP. Further details on the measurement of the protein band intensities are described in Materials and Methods. Quantitation is for the specific experiment shown, but is representative of multiple independent experiments.