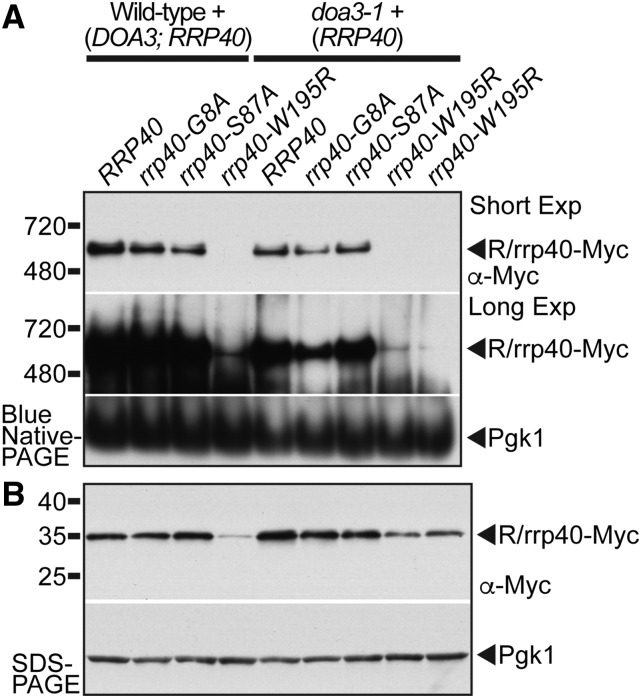
Figure 7.
The rrp40-W195R variant associates less efficiently than wild-type Rrp40 with the RNA exosome complex in S. cerevisiae cells coexpressing wild-type Rrp40. (A) Unlike wild-type Rrp40, only a low amount of the rrp40-W195R variant in doa3-1 cells migrates as a 600 kDa complex that is consistent with the size of the 11-subunit exosome (Liu et al. 2006) by native gel electrophoresis. In contrast, a similar amount of rrp40-G8A and rrp40-S87A variant compared to wild-type Rrp40 migrates as a 600 kDa complex. Lysates of wild-type and doa3-1 temperature-sensitive proteasome mutant cells expressing Myc-tagged wild-type Rrp40 or variant rrp40 (G8A, S87A, and W195R) were grown at 37° and analyzed by BN-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-tagged Rrp40 proteins (R/rrp40-Myc) and anti-Pgk1 antibody to detect Pgk1 as a loading control. (B) In the same lysates analyzed by native PAGE in (A), the amount of rrp40-W195R variant in doa3-1 cells is increased and stabilized relative to wild-type cells analyzed by denaturing SDS-PAGE. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-tagged Rrp40 proteins (R/rrp40-Myc), and anti-Pgk1 antibody to detect Pgk1 as a loading control.