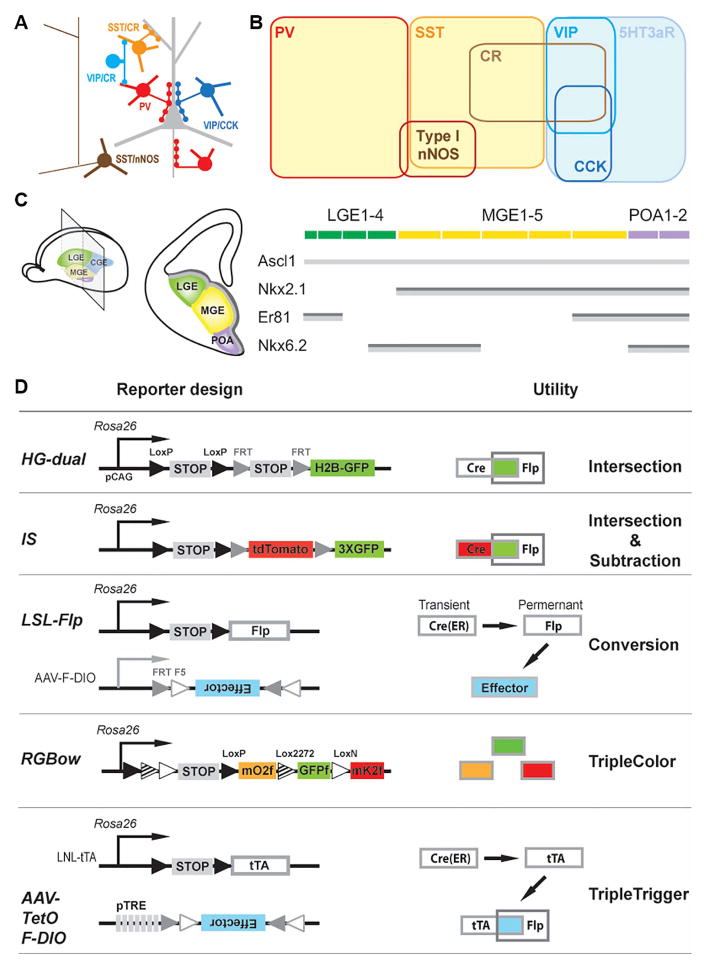
Figure 1. Combinatorial strategies and tools for genetic targeting of cortical GABAergic neurons.
(A) A schematic of several major GABAergic neuron types in the neocortex. (B) Major neurochemical markers expressed in cortical GABAergic neurons. (C) Left: Schematic of subpallium progenitor domains in the embryonic telencephalon and its coronal view at the indicated plane (middle). Right: Schematic representation of expression patterns for four transcriptional factors, Ascl1, Nkx2.1, Nkx6.2 and Er81, along the subpallium progenitor domains. Dark grey bar: ventricular zone consisting of mostly radial glia cells. Light grey bar: subventricular zone consisting of mostly intermediate progenitors. (D) Diagram of reporter and viral strategies. Newly generated tools are in larger font. PV, parvalbumin; SST, somatostatin; CR, calretinin; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide; CCK, cholecystokinin; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; MGE, medial ganglionic eminence; CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; POA, pre-optic area. (See also Table 1, Figure S1–2, Table S1–3.)