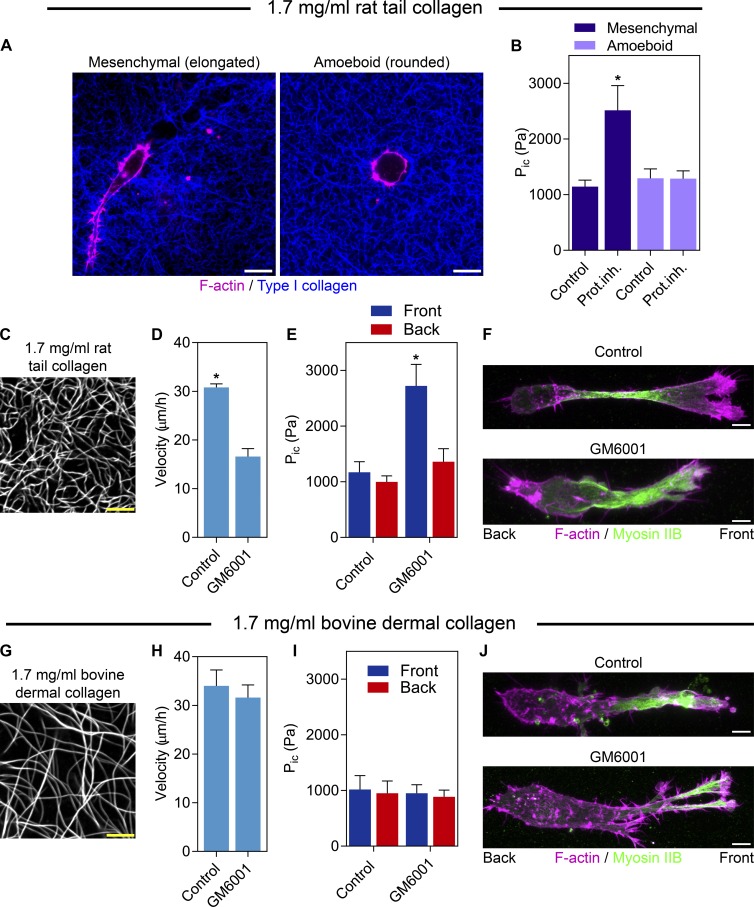
Figure 3.
Protease inhibition increases compartmentalized pressure in mesenchymal tumor cells in low-porosity 3D collagen. (A) HT1080/ATCC cells in 1.7 mg/ml 3D collagen use either the mesenchymal (elongated) or amoeboid (round) modes of tumor cell migration. Bars, 10 µm. (B) Intracellular pressure (Pic) does not differ significantly between amoeboid and mesenchymal tumor cells moving through 3D collagen. Upon addition of 10 µM GM6001, intracellular pressure specifically increases in mesenchymal tumors cells, whereas the pressure in amoeboid cells does not change (n = 30, N = 3). 1.7 mg/ml rat tail (C) and bovine dermal (G) collagen labeled with Alexa 647. Bars, 5 µM. MMP inhibition significantly slows the velocity (n = 45, N = 3; D) and increases compartmentalized pressure (n = 15, N = 3; E) of HT1080/ATCC cells moving in rat tail collagen, but not bovine dermal collagen (H and I). Myosin IIB localization is unaffected by GM6001 treatment in 1.7 mg/ml rat tail (F) and bovine dermal (J) collagen (n = 15, N = 3). Bars, 10 µM. Error bars indicate SEM. *, P < 0.01 versus control cells.